
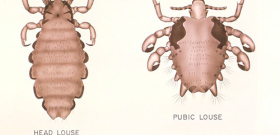
Species of lice, generally speaking, are numerous - only in mammals there are more than 500 species of these insects. At the same time, only two different types of lice parasitize on humans - the human louse (Pediculus humanus) and the pubic louse (Pthirus pubis). They quite easily differ from each other both externally and in the places of their habitat and parasitism.
It is often incorrectly believed that there are not two, but three types of lice in humans: for example, head and body lice are also distinguished. However, these are not separate species, but only forms (scientists call them morphotypes) of human lice, peculiar varieties of lice. They are adapted to living in different conditions: the head one - in the hair of the head, and the clothes (linen) one - on clothes - and during the time of parasitism on a person they managed to develop such differences in their lifestyle that they almost never intersect or interbreed on the human body. Laboratory studies have shown that they have not yet come to a complete separation into different species, and if they exist together (possible only under artificially created conditions), they are able to interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
The photo below shows different types of lice in humans - human and pubic:


And in the next photo - a variety of lice in humans. The first is a head louse, the second is a clothes louse:


On a note
No matter how numerous lice are in nature as a whole, their species are specific in that they are adapted to life on only one type of host animal. So, human lice cannot live on the body of other mammals, with the exception of a few species of monkeys, and dog lice live only on dogs - and so on.
That is, a person can become infected with lice only from another person, but not from animals. In this respect, lice differ significantly from fleas. The latter are similar in size, but can parasitize a large number of animal host species.
All varieties of lice in humans are similar in that the full cycle of their reproduction takes place on the host's body or in its immediate vicinity - on hair or clothing. All types of lice that a person has feed exclusively on blood, and unlike other parasites, each individual bites the victim several times a day - most blood-sucking insects feed once every few days (for example, bed bugs), or even weeks.
head louse
The head louse is the most common parasite and often occurs even in people living in normal sanitary conditions. This insect infects only the scalp, only in exceptionally rare cases moving in men to sideburns and beards.
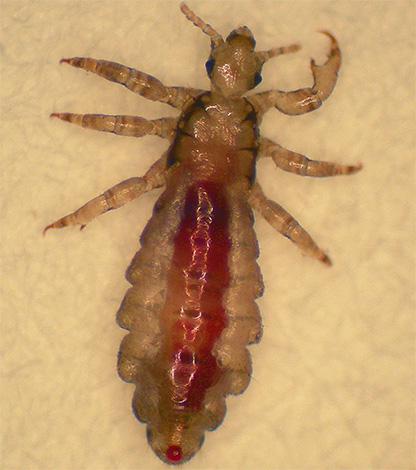
In general, this type of lice differs from clothes lice in a slightly darker body color - it is grayish-brown. After feeding, the body color of the insect becomes darker than it was before, due to a drop of blood in the stomach. The photographs below show several insects of this form:
And further: Killer remedy for lice and nits for 40 rubles - hellebore water (the article has more than 60 comments)


The main difference between head lice and linen lice is the difference in their habitats.
The size of adult head lice is about 2-4 mm. Lice larvae are about 0.6-2 mm in size. The eggs of head lice are called nits and are firmly attached by the female laying them to the hairs at a distance of about 2-3 cm from the surface of the scalp.

Head lice breed constantly regardless of the season. They feel great at a temperature of 30-33°C, and continue to breed in the temperature range from 23°C to 40°C. Lice die when the temperature drops below 0°C or rises above 45°C.
Without hair on the head, this kind of lice cannot live. In the picture below - a louse crawling along a bun of hair:

Accordingly, the simplest and most reliable way to get head lice out of your head will be a “naked” haircut. In other cases, you should use shampoos, sprays or creams containing insecticides, or special hard and thick combs from lice and nits.
Cootie
Clothes louse (another name is linen louse) looks very similar to the head louse and has a similar body structure with an elongated abdomen, as well as similar sizes. It differs from the head louse in body color - it is usually white or light gray with a yellowish tinge, and, of course, in habitats.
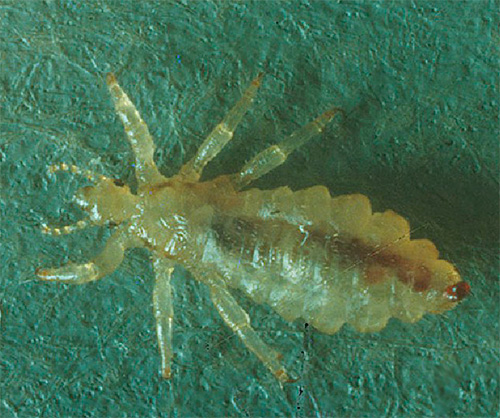

The body louse is adapted to life only on clothes that are constantly or very often on the human body. She cannot live on hair or in clothes that a person wears very rarely. Therefore, most often the victims of body lice are vagrants, refugees and antisocial individuals who do not change their wardrobe and rarely wash their clothes.
The photo below shows this type of lice - you can see the accumulation of parasites on the fabric:

The body louse bites a person under clothing and in most cases - on hairless areas of the body.
These parasites lay their eggs (nits) on clothes, and therefore the fight against them is usually simpler than removing head lice: here you need to either boil or treat the things themselves with dangerous means for lice, and wash the body thoroughly to simply wash off the remaining on it insects.
On a note
All lice can withstand a sufficiently long immersion under water. When washing the head and hair in the groin area, the lice themselves, clinging to the hair, are not washed off, and even more so, the nits remain unharmed. Individuals that are on the skin at that moment can only be washed away.
pubic louse
Of all the types of lice in humans, the pubic louse is the smallest. An adult individual reaches a length of no more than 2 mm, and larvae of the first age - only about 0.5 mm. Without a microscope, these insects look like small, slightly flat, brownish dots.
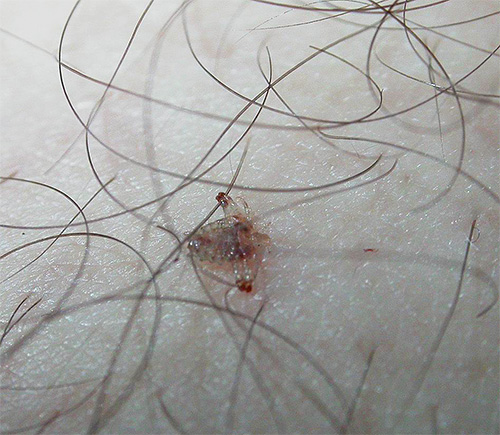
Pubic lice affect almost exclusively the hairy part of the body in the groin, but in very rare cases they can also settle in the armpits, and in some cases (especially when infected by water) - on the eyebrows and eyelashes:
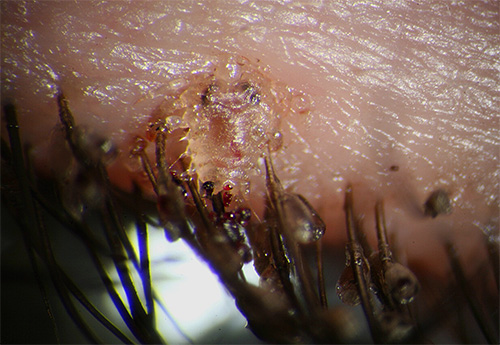
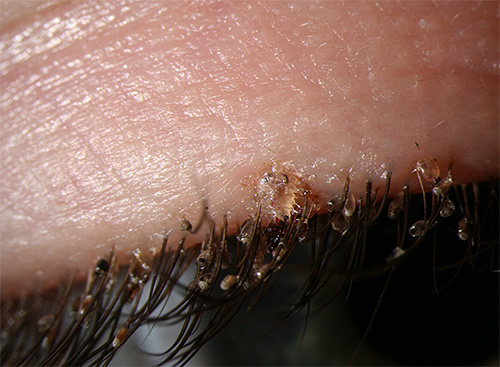
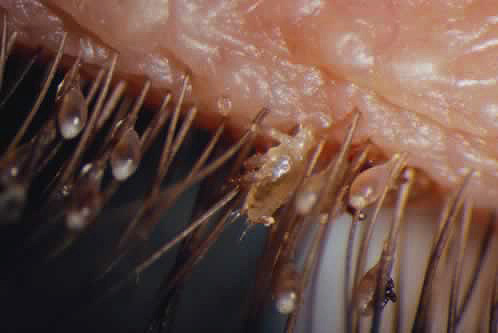
Under the microscope, the difference between the shape of the body of the pubic louse and the human louse (head and body lice) is clearly visible - the parasite is much shorter and has legs that are more massive relative to the size of the body. The photo below shows both types of lice at high magnification:
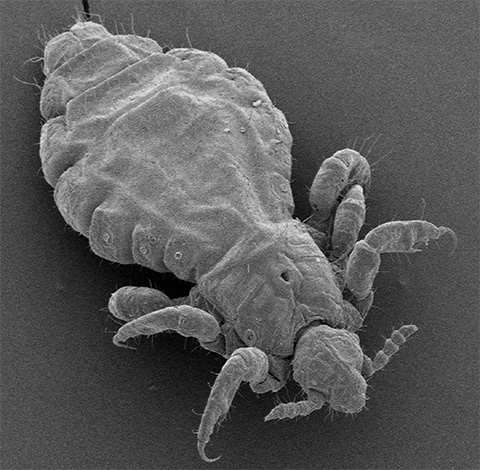

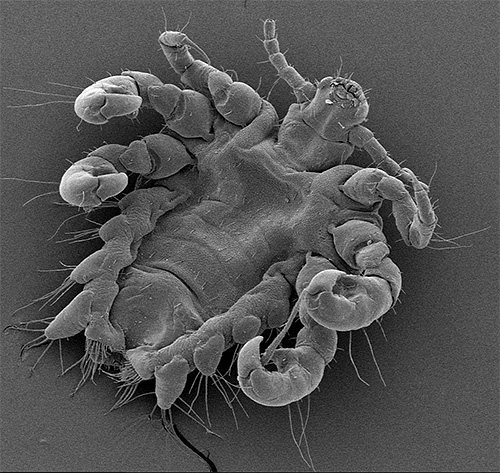
Pubic lice are most often transmitted through sexual contact, and therefore infection with them is considered a kind of venereal parasitosis. However, in some cases, pubic lice are transmitted through water or shared clothing.
It is interesting
In recent years, experts have noted a decrease in the incidence of pubic lice and a decrease in the number of this parasite in general. It is believed that one of the reasons for this is the fashion for shaved pubes, because of which insects are deprived of the only conditions suitable for their existence.
Lice in other animals
In other animals, lice species are much more diverse in size and body shape.
For example:
- Hare louse, which has a hairy and very dense body. It parasitizes several species of hares and rabbits.
- Pig louse, quite large and having a body length of about 5 mm. Settles behind the ears, on the folds of the neck, abdomen and legs of domestic pigs and wild boars.
- A dog louse belonging to the order of the Vlas-eaters. In addition to the blood of the host, it can also feed on pieces of skin and secretions from the skin glands of the animal.
- Elephant louse, which has adapted to the lack of hair in the host by having a proboscis expanding at the end, due to which, when bitten, it clings tightly to the skin.
The photo below shows some of these types of lice. All species that live on animals are not dangerous to humans:


In addition to the actual lice, the lice in animals are also very well known. There are more than 3,000 species of them, and they lead a lifestyle similar to lice. Their main difference from true lice is the ability to feed not only on blood, but also on various derivatives of the host's skin. Birds are even more numerous, but they are distinguished from lice by even more features.
Considering what lice are, one cannot help but recall the famous book louse.


It is not a typical louse, but belongs to the suborder of hay eaters and feeds on various organic residues: from various groceries to book bindings. It is not dangerous to humans directly.
What you need to know about human lice
Interesting video: details about lice and methods of dealing with them



I had lice and nits, but not the same. I tried Para Plus before, but it did not help me. Mom looked at me now, she found 2 nits, but there are a lot of lice. Mom should buy Paranit for me, and Paranit will help me.
I had only 1 louse in the summer, my mother ordered Nyuda and I don’t have them anymore.
Buy NUDE (NUDE), she is very good! It is sold in pharmacies, it acts immediately after application.
And Nyuda will help me forever.
I have this problem too.
Lice in a child for the second time. They don't disappear. Already tried everything, does not help.Tell me, please, how to treat?
Hellebore water costs a penny, helped me 3 times.
Pediculen ultra
Hellebore water - quickly and easily.
Photos of lice on clothes - fu, there were, we know. No more.
How did you get rid of it?
If anyone has lice, make pills - roll 1 piece into a bread crumb (certainly alive, they have some kind of enzyme that heals the human liver, which is quickly destroyed when this insect dies) and swallow. Do this 1 time in 3 days. This will get rid of many liver diseases (for example, hepatitis) or their consequences. During the war, my great-grandmother saved so many people and told me this simple recipe. Botkin is treated quickly and without complications. She said that sometimes it was difficult to find lice, then they bought from gypsies. Therefore, do not immediately destroy, but heal yourself and help your loved ones before that. By the way, if you don’t believe, you can google it, a lot of people have been cured this way, and many are looking for it) I don’t call for business, but ...
I have the same problem. And Para plus helped me.