
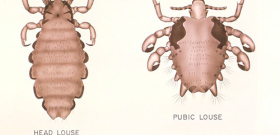
The human head louse is, so to speak, a double nuisance. By itself, as a parasite, it causes a lot of problems and discomfort, feeding on blood and causing multiple itchy bites. Her saliva and general activity on the scalp can lead to the development of a whole range of symptoms, which, due to their specificity in medical practice and theory, are singled out as a separate disease - pediculosis.
However, pediculosis itself and the presence of lice on the head are only part of the problem. The fact is that the diseases spread by the human head lice are not only severe - they are also deadly.
But first things first…
Human head louse as a parasite
Lice are already dangerous for humans even just as parasitic insects. After all, their main food is human blood, which they suck out by piercing the skin with jaws that have the shape of thin and long stilettos.
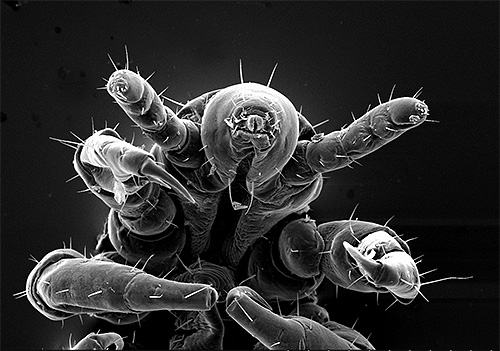
Given the small size of the parasites and the rather low density of human infection with lice, the very fact of bloodsucking in most cases does not lead to a noticeable decrease in the amount of blood in the capillaries, and even more so, to a change in the composition of the blood itself.However, even without this, multiple bites are already causing trouble.
First of all, it is the itching caused by each single puncture of the skin, during which the insect injects its saliva into the wound. Such a bite is similar to a mosquito, however, in general, the bites themselves occur much more than when attacked by mosquitoes. The specificity of human lice is such that each insect is forced to eat little and often. In one day, one louse makes four or five bites, and if there are several dozen parasites on the head, their constant feeding will be associated with hundreds of daily bites.
In addition, lice constantly move around the head and this also irritates the surface of the skin.

However, these are the most insignificant consequences of a person having lice. Much more serious diseases, the pathogens of which lice carry, and those disorders, the direct cause of which they themselves are.
Pediculosis is the main consequence of lice infestation.
Pediculosis is a disease associated specifically with the activity of lice. It is a complex of symptoms resulting from regular bites by parasites, during which saliva containing enzymes is injected, and constant irritation of the nerve endings.
The most characteristic symptoms of pediculosis are:
- itching on the head, at a certain stage becoming permanent
- the appearance of bluish-gray spots on the skin
- permanent scratching of the scalp
- excessive keratinization of the scalp and dandruff
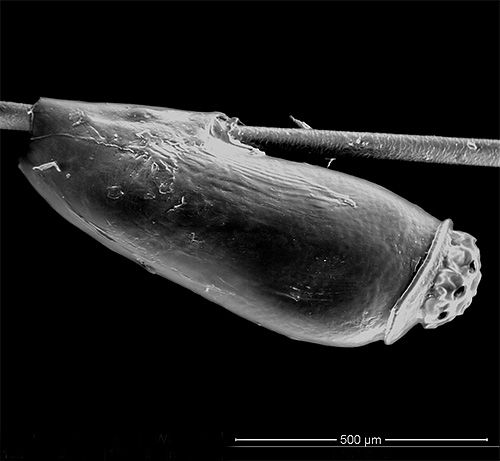
- as well as the presence of lice themselves on the head and the presence of nits (lice eggs) attached to the hair at different distances from the surface of the head.
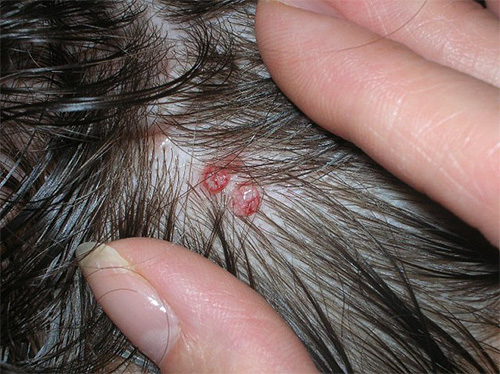
Such symptoms usually appear a month and a half after the infection itself.During this time, lice that have fallen on the head have time to give the first offspring and significantly increase their numbers on the head of a person.
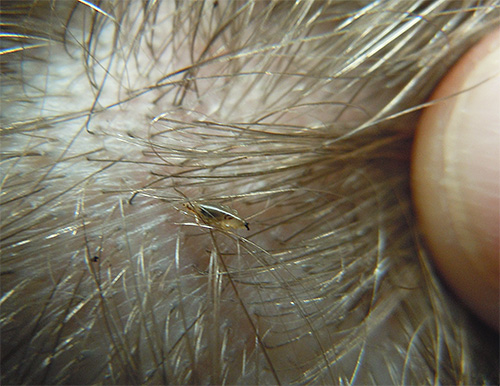

It is interesting
In the people, the period from infection to the appearance of obvious symptoms of pediculosis is called the incubation period of lice. From a scientific point of view, this term is inappropriate here.
Due to scratching of the scalp, if left untreated, pustular inflammation can develop in those places where an accidental infection enters the bloodstream. Such injuries are already painful and require a visit to the doctor to develop a treatment plan.
And further: It's time to finally get those annoying nits out of your hair (the article has over 100 comments)
Pediculosis is not a life-threatening disease. But besides him, lice carry pathogens that at one time led to huge mass and devastating epidemics.
Lice as carriers of dangerous diseases
Diseases spread by human lice are caused by rickettsiae, bacteria from a special family, some of which are extremely pathogenic. Among these diseases:
- typhus
- relapsing fever
- quintan
…and some other related infections.
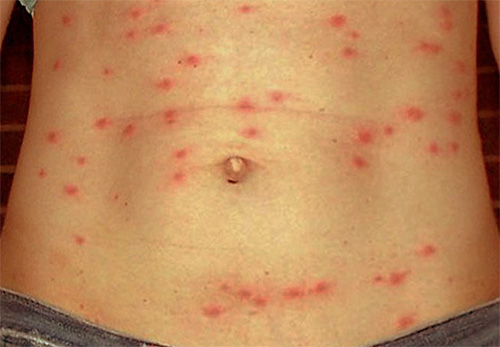
All types of typhoid are characterized by acute course, the possibility of death and a weak immune response of the body: even after suffering the same relapsing fever, immunity is established for a short time. Volyn fever is not a fatal disease, but also very unpleasant.
It is interesting
According to doctors, during the Russian-Turkish wars, more soldiers died from typhus than in the hostilities themselves.The conditions in which the soldiers lived and were ideally suited for the development of diseases that human head and body lice carry.
In most cases, body lice are carriers of dangerous infections. The probability of contracting typhoid from head lice is lower than from body lice, but due to its greater prevalence throughout the world, the head louse causes various diseases in general, not much less often than body lice.
Do lice carry AIDS and hepatitis?
There is a widespread belief that blood-sucking insects can carry viruses that cause AIDS and hepatitis. Accordingly, lice are sometimes suspected of carrying these terrible diseases.
Lice do not tolerate AIDS or hepatitis. Both of these diseases are caused by viruses that infect the cells of the internal systems of human organs. The AIDS virus invades the cells of the immune system, while the hepatitis virus invades the liver cells. And these viruses are indeed present in the blood of a sick person.
And further: Creepy photos of head lice, including macro photography (the article has more than 50 comments)
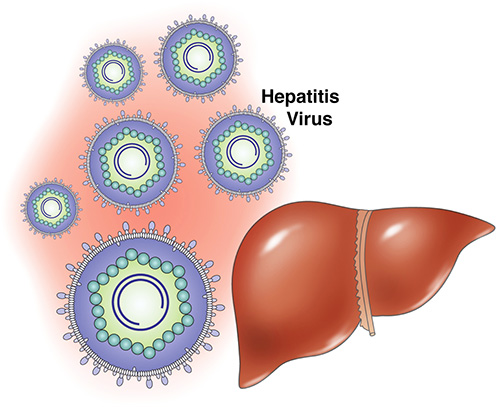
However, these viruses cannot infect lice and use them as intermediate hosts. Getting along with human blood into the digestive tract of insects, virions - virus particles - are quickly split by insect enzymes and cease to exist.
On the oral organs, viruses do not persist for a long time and are washed off by mucus, which acts as saliva in parasites. Accordingly, even after the bite of a sick person, the viral particles in the parasite cease to exist, and by the next bite, even on another, healthy person, the louse will already be “clean”.
On a note
Similarly, AIDS and hepatitis are not carried by mosquitoes and ticks. Parasites can only carry those diseases, the pathogens of which in their life cycle are somehow connected with these parasites. For example - tick-borne encephalitis, malaria (caused not by a virus, but by protozoa), sleeping sickness. Rickettsiae are associated with lice, carrying typhus and related diseases. AIDS viruses and all hepatitis pathogens (including bacterial ones) are not associated with lice and are not spread by them.
To date, in medical practice, there are no known cases of transmission of AIDS and hepatitis viruses by lice. All speculations about such a transmission route are considered imaginary dangers and are not supported by any research.
On a note
Another misconception is the myth that lice can treat hepatitis. This is also stupidity - the louse does not affect the course of this disease in any way, especially since hepatitis can occur for a variety of reasons.
The first signs of infection with lice and typhoid
It should always be remembered that typhus and other diseases transmitted by lice have an incubation period shorter than the time of manifestation of pediculosis itself. Simply put, after being infected with lice, a person becomes ill with typhus (provided that the lice themselves in a particular case were carriers of the pathogen) before they begin to feel serious signs of the appearance of lice.
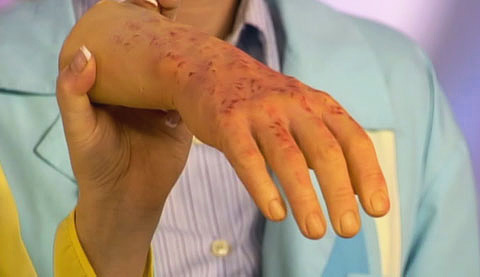
The incubation period for typhus is about 2 weeks, and relapsing fever is about 18 days. The first symptoms of the disease are pain in the head and back, fever, chills, fever. During the first week of the manifestation of these symptoms, with typhus, a pinkish rash also appears throughout the body, with a return - yellowness of the skin.Usually, both diseases are characterized by several attacks, after which recovery occurs.
On a note
An effective vaccine has been developed against typhus, which allows you to protect the vaccinated person for several years. This vaccine is not included in the list of mandatory, but when visiting regions where the likelihood of contracting the disease is high, it is strongly recommended to use it.
Deaths from typhus are caused by disorders in the circulatory system, and most of them are due to blockage of the pulmonary artery. Common complications of the disease are disorders of the nervous system and thrombophlebitis.
Volyn, or trench fever, proceeds similarly, but without pronounced manifestations on the skin. After the second or third attack, there is usually a complete recovery.
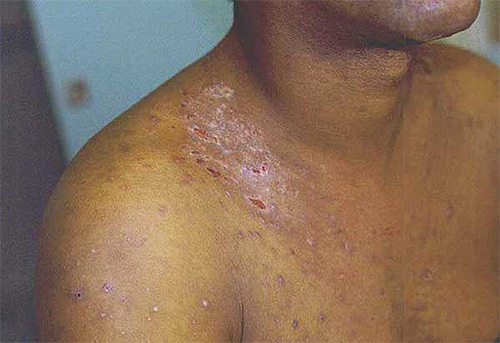
At the first such symptoms and the presence of lice on the head, you should immediately contact a medical institution. Self-treatment of such diseases can lead to serious life-long complications.
All diseases spread by human lice are very rare today. Typhus and various rickettsiosis appear almost exclusively in developing countries in conditions of unsanitary conditions and too dense settlements of people. They are typical mainly for the countries of Africa and South America.
It is interesting
One form of typhus, Brill's disease, which is dangerous for its relapses, is sometimes recorded in the eastern United States.
In modern conditions, the main guarantee of safety from diseases carried by lice is the prevention of infection by the parasites themselves.To do this, you should avoid accidental close bodily contact (hugs, kisses, sexual contact) with strangers, try not to be in places with a large crowd of people and obvious signs of unsanitary conditions, do not use other people's combs, towels and hair care products.

If you do not give lice a chance to get on your head, then infection with the corresponding infections can be avoided.
What is important to know about lice for any civilized person



My head is itching!
Maybe you have lice too.
I started right away too! And now I'm scared! Brr...
And I'm scared.
Can lice carry streptoderma?
I'm scared too, they transmit diseases...