
Entomologists, strictly speaking, do not know such an insect as a moose flea. Among the existing species of fleas, moose fleas are absent, and even animals close to them - for example, deer and roe deer - do not have their own varieties of fleas.
But on the elks themselves and other ungulates of the taiga, a whole range of blood-sucking insects can indeed parasitize: here are the fleas familiar to us, and blood-sucking parasites from completely different orders.
Among the people, all crawling and jumping blood-sucking parasites that pester large animals of the taiga and which sometimes attack humans are often called moose fleas. Among them:
- goat fleas, more common on roe deer than elk
- Alakurt, parasitizing mainly on sheep, but capable of attacking larger ungulates
- deer bloodsuckers are parasitic flies that, after falling on the hair of an elk or deer, lose their wings and move to a permanent residence on the host's body.



The first two species of insects are typical fleas: their biology and appearance are similar to cat and rat fleas.The deer bloodsucker is exactly a fly, but due to the fact that it is most often found crawling in wool, it was also dubbed a flea.
Let's take a closer look at all these insects and find out what danger they can pose to humans and how to protect ourselves from them.
Alakurt, or sheep flea
Alakurt is known primarily to the shepherds of the high mountain pastures of Altai and Sayan. This large flea thrives mainly in the thick and long wool of domestic sheep, but parasitologists have also found it in wild roe deer and gazelles.


Alakurt is remarkable primarily for its size - females with developing eggs can reach a length of 10-12 mm! Because of the greatly increasing in size and brightening abdomen, the locals call this parasite the "white worm".
Alakurts can live on animals in large numbers. A distinctive feature of these fleas is that they are constantly present on the body of the host, which distinguishes them from other representatives of the order of fleas.
It is interesting
Most species of fleas parasitize animals that have a permanent place to sleep or shelter. It is in the host's nest that parasites spend most of their time and reproduce. These species include rat, rabbit, cat, dog and some other fleas.
But those species of fleas that parasitize on ungulates are forced to adapt to the constant presence on the host's body - deer, elk, fallow deer, gazelles and other ungulates rarely return to the same place to spend the night, and therefore the flea has a chance to find after rest host in a large forest or steppe pasture are small. As a result, the lifestyle of these flea species becomes similar to the lifestyle of lice that constantly live on their host.
In some cases, with a serious infection, alakurt can lead to the weakening of the animal and even its death. For humans, this flea is not dangerous, and cases of its attacks on humans are unknown.
Goat fleas can also attack deer and elk.
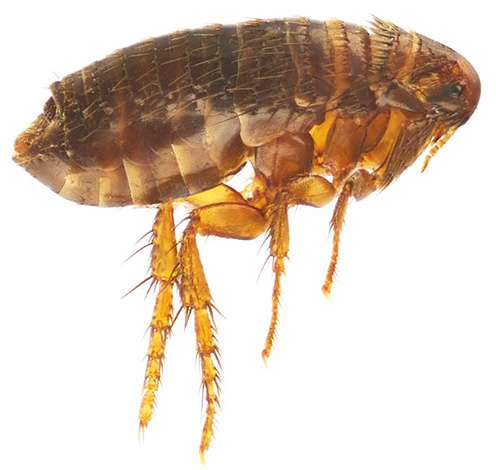

They can also bite humans. These insects differ little from dog and cat fleas, and therefore, when they hit the human body, they do not attract much attention to themselves.
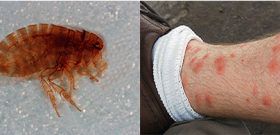
Deer bloodsucker, its appearance and lifestyle
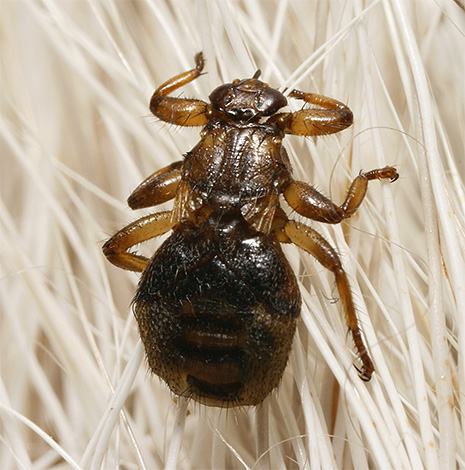
The deer bloodsucker is a large and rather mobile fly. It is also called elk tick, elk flea or deer lice. It has a characteristic rather “strong physique” and strong paws, its body length is 3-4 mm.
In the photo - a moose flea during the period of constant parasitism on the host:


The whole life of a moose flea is divided into two stages. The first is the search for the owner. It begins from the moment the fly hatches from the puparia, a kind of chrysalis in which the insect survives the winter and develops during the spring and summer. In central Russia, the bulk of young deer bloodsuckers appear in August-September, but in general, the period of emergence of young individuals extends from June to November.
A young fly lies in wait for the future owner on the branches of a bush or in the grass.

Seeing or sensing the victim, the insect slowly flies towards it (bloodsuckers are unimportant flyers), and when it gets on the wool, it clings tightly to it and after a while sheds its wings. The second stage of the life of the parasite begins - feeding and reproduction.
For bloodsuckers, life in pairs is characteristic - the male and female, having met on the animal, are constantly nearby.So, if there is one fly on the dog after a walk in the forest, then with a high probability you can find a second fly somewhere in the wool.
After mating, the female begins to actively feed, and one larva develops in turn in her uterus. For bloodsuckers, live birth is characteristic - the female gives birth to a formed and developed chrysalis, which, having fallen to the ground, hardens and continues its development only six months later - in the spring.
The flies are also active in the animal's fur in winter, continuing to lay puparia. As a rule, by spring the parasites die.
Below is a photograph of a winged moose flea:
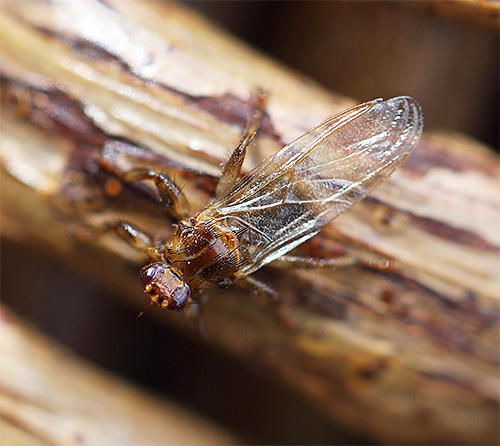

Moose fleas attack animals and people only during the day, when they can see the victim. Especially often they attack hunters when they process a seriously infected carcass of an elk or deer.
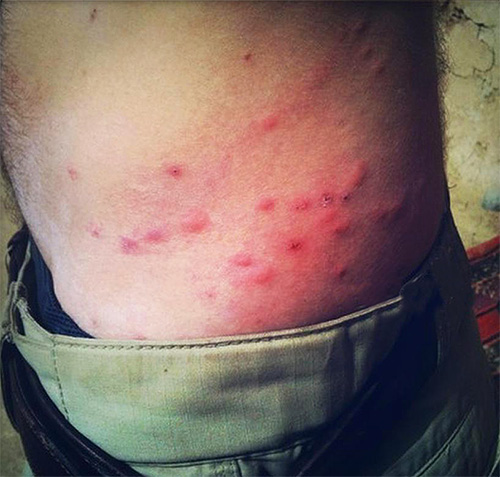
Flea bites that parasitize moose and deer
The bite of a moose flea is very painful, especially for an unusual person. Those who are often in the forest and are attacked by mosquitoes sometimes do not even feel the bites of bloodsuckers.
It is interesting
In order to give birth every few days to a developed larva, the female bloodsucker must suck the blood of the host 15-20 times a day, every hour and a half. In one bite, the insect sucks out 0.5-1.5 mg of blood. The male feeds less intensively.
On some shot animals, hunters found up to 1000 moose fleas - every hour such an army of parasites sucks a gram of blood from an animal, and besides, it constantly leaves itchy bites that can become infected with bacteria and abscess. Often, bloodsuckers bring diseased animals to complete exhaustion.
If we talk about the danger to humans, then it is worth noting that moose fleas attack almost exclusively adults.Children are less "interesting" to them - perhaps the size of the victim plays a role here.
According to some estimates, hunters in the forest were sometimes attacked by up to 100 parasites per minute. In this case, the fly tries to get under the clothes or in the hair. It is difficult to remove it from the surface of the skin due to its small size and flat body.


At the site of a moose flea bite, a red spot appears in a person, and a little later, a characteristic papule. Sometimes itching appears after this, but rashes and an allergic reaction are usually not observed.
Moose fleas do not tolerate pathogens that are dangerous to humans.
It is noteworthy that the more a person is bitten by bloodsuckers, the more acutely he reacts to their subsequent attacks.
How to avoid moose flea bites?
It is almost impossible to avoid the attack of bloodsuckers in the forest. If an insect sees or feels a person, it will definitely fly up to him. But to ensure that the parasite does not get on the skin and does not bite - it is quite possible.
For this you should:
- wear clothes that cover the whole body;
- tuck pants into shoes or socks;
- use a mosquito net;
- use powerful repellents based on DEET. The content of DEET itself in them should be at least 20%, preferably up to 100%. Feeling this substance, the flies will not dare to bite.

It is very useful to go to the forest with a partner who will regularly check the hair and neck for moose fleas and other parasites. By the way, in the forest it is useful to check each other for stuck ticks.
After staying in the forest, especially after a successful hunt, you should take a bath and wash your body and head with tar soap. This will remove already settled bloodsuckers from it.
An interesting video: this is how, in fact, a deer bloodsucker, or a moose flea, looks like



Deer Bloodsucker flew into my house. Since I have long hair, she very quickly moved over each of my hairs to the scalp. But I suddenly felt that something was teeming in my hair, so, holding this blood-sucking creature tightly with my fingers, I pulled it out of my hair. I didn’t have time to bite me, because I didn’t feel any pain.
This parasite is indestructible. I crushed his wings, but the body itself did not. Try to always wear caps and panama hats in the summer (especially in the month of August), when you walk in the forest or where there are a lot of trees. They are not dangerous to humans, but still not fully understood. And what kind of skin diseases they can bring to us has not been fully established.
Today for the first time I encountered this creature, I caught as many as five pieces in the forest on myself ... A rare muck. Thank God, we didn't have time to bite.Now it feels like they are running all over the body. Is that why there were not so many of them in our region before? Are there a lot of deer and elk?
The dog brought 5 pieces on itself. While I was catching them, these insects got over to me. One caught on the neck, and the second in the hair! Thank God, we didn’t have time to bite 🙂
Twice I went to the forest and each time brought them home. I found it only late at night when I went to bed. Then all night long it seemed that someone was crawling on me. The disgust is indescribable...
There are a lot of them divorced not far from St. Petersburg. After coming from the forest, it happens that I find on myself more than 100 pieces.
In the Volosovsky district of Len. their areas are unmeasured. Each trip for mushrooms turns into torment. They get into your eyes, ears, and then at home you pull them out for two hours. This was not the case before.
The Saturday before last, elk fleas attacked in the forest. He came to the car, turned the T-shirt inside out, collected 100 pieces. They didn’t bite, but two days later, acne on the back, neck and stomach spilled out. Periodic itching. Smeared with iodine and alcohol. Just today I went to a dermatologist, the doctor did a scraping and said that parasites clearly live under the skin (suspected of demodicosis). Tomorrow I will know the test results. In short, tin. And you don't know if it's because of them or not