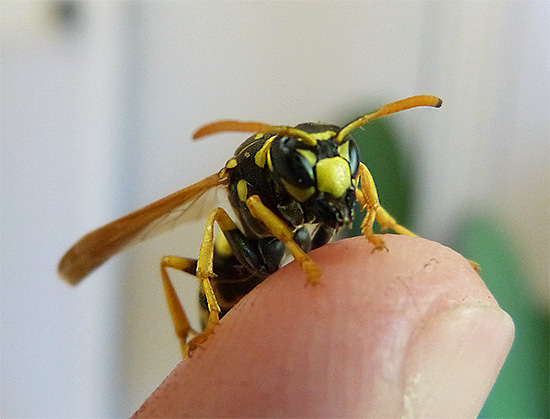

Few people do not know what a wasp sting is: its consequences are familiar to almost every adult, and many from memory from childhood. Severe pain, redness, swelling and itching - this is the standard reaction to a wasp sting.
Meanwhile, the consequences of the attacks of these insects can be much more severe. Why is a wasp sting dangerous? Let's figure it out...
First of all, the bites of hymenoptera insects (which include wasps, hornets, bees, and some others) are distinguished by their high allergenicity. In addition to toxins that destroy the cell walls of affected tissues and affect nerve endings, wasp venom also contains substances that can cause a powerful immune response in the body.
If a person does not have a hypersensitivity to wasp venom, he may not feel these allergens. If the victim is hypersensitive (such people are also called sensitized), a wasp sting can be even more dangerous for him than, for example, an attack by a poisonous spider.
Review
“I received an allergy card last summer after a wasp sting.I always treated them with indifference, because my grandfather was a beekeeper, so all my childhood I went bitten by bees. The doctor said that because of this and all the problems.
Near the dining room at work I was bitten by a wasp, the temperature rose, my head began to hurt, a rash appeared on my face. She came home almost unconscious, her whole body was sprinkled. It's good that my daughter immediately called an ambulance. They pumped me out. They said it was very bad. Then the doctor looked, took tests, said that I had a very high sensitivity. And that if you don’t have a special syringe with medicine with you, then death from a wasp sting is quite possible for me. Such are the things."
Veronika, Zelenograd
The most unpleasant thing here is that no one really knows whether he has such sensitivity or not. It can be congenital, or it can develop over time in response to the bites of various insects. Therefore, complications after an attack of wasps can arise unexpectedly and for anyone.

On a note
A fatal wasp sting is a rarity, but this sometimes happens. For example, in the United States, more people die each year from hymenoptera attacks than from snake bites. Moreover, not so much depends on the type of insect here: both the sting of an ordinary paper wasp and a honey bee can be fatal.
Wasp venom and its specificity
Wasp venom in its composition is in many ways similar to the poisons of other hymenoptera - bees, hornets, bumblebees, some tropical ants - but it also has its own characteristics.

Here are some of the active components of wasp venom:
- phospholipases causing destruction of cell walls, tumor and inflammation;
- melitin - a component that promotes hemolysis (destruction) of mast cells;
- apamin - a toxin that has a strong effect on the nervous system, including motor nerves;
- acetylcholine, which has a direct effect on the conduction of nerve impulses;
- histamine, the main function of which is to start the mechanism of an allergic reaction (it is the neutralization of histamine that the action of antiallergic drugs, which are called antihistamines, is aimed at);
- MCD-peptide, which destroys mast cells and causes an avalanche-like increase in the amount of histamine in the blood (as a result, the development of an allergic reaction is accelerated);
and some others.
Partly due to the destruction of cell walls, the wasp sting often hurts for a long time and passes rather slowly: inflammation develops in the affected area, which disappears as the cells recover. When the walls of small blood vessels are destroyed, hemorrhage occurs - this is especially pronounced with hornet bites.

The reaction of people to the action of wasp venom is largely individual. On average, in a healthy person, a wasp sting hurts for several days, and its consequences completely disappear in a week and a half.
In different types of wasps, the poison has a different composition. So, for example, the bite of the so-called road wasp, long and slender, is considered one of the most painful among all insects known in the world (the bite of a tropical bullet ant is even more painful). But the bites of wild wasps (paper, whose nests can be found, for example, on trees in the forest) are not much different from the bites of these same insects, but building their nests, for example, in summer cottages.

It is interesting
There are very large predatory philanthus wasps that feed on bees.Their bite is generally insensitive, and beekeepers catch and crush them with their bare hands. On the contrary, small wasps, the size of a house ant, live in open spaces, which bite about as painfully as ordinary paper ones. Therefore, the bite of some forest wasp that is not quite familiar in appearance can be unpredictable in its consequences.
What does a wasp sting look like
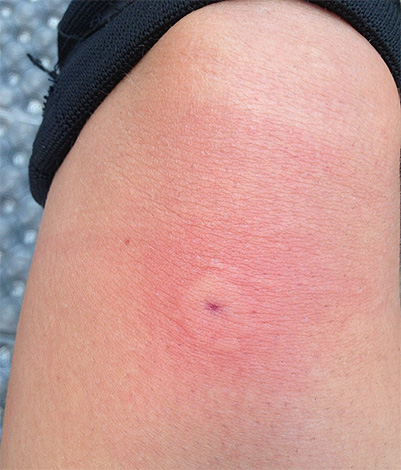
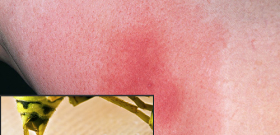
Usually, the trace of a wasp attack looks like a large reddish bump, in the center of which you can often see a puncture left by an insect sting.
The photo below shows a fresh wasp sting mark:
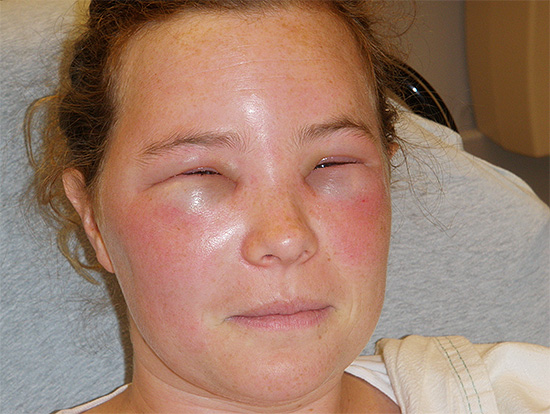
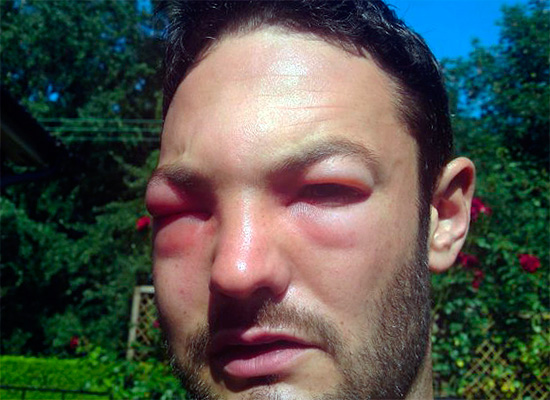
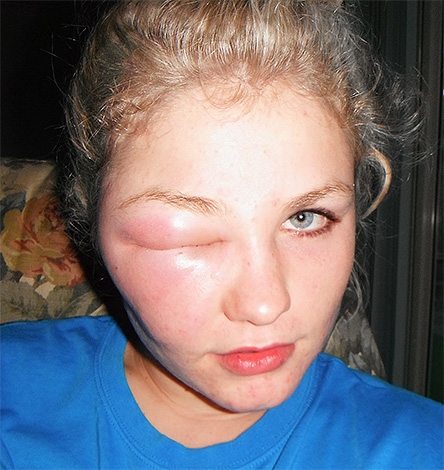
Sufficiently "bright" (and dangerous) consequences can be observed in cases where a person has an increased sensitivity to insect bites - in this case, an allergic reaction sharply enhances the external manifestations of the bite. For example, a wasp sting in the face sometimes leads to the fact that a person simply cannot see, as the face is very swollen, and both eyes close. And a wasp sting on the tongue, which is quite rare, can cause it to swell so much that the victim will not be able to close his mouth.
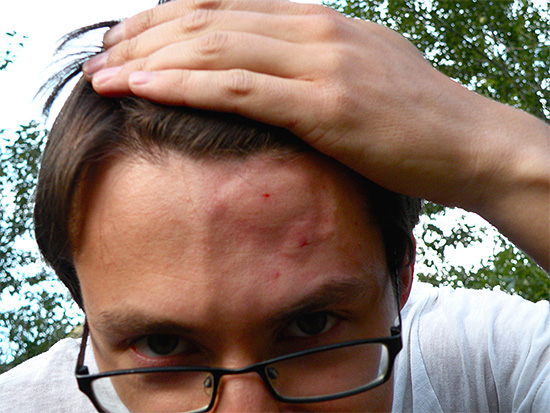
In the photo below - the consequences of a wasp sting in the face:
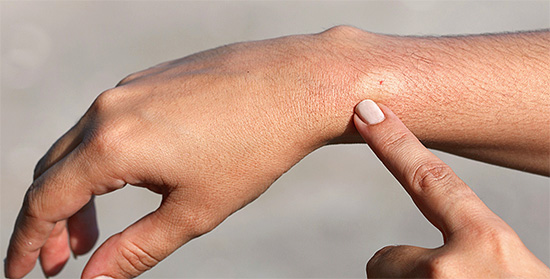
Conversely, in some people, a wasp sting in the head can be almost invisible outwardly.
Review:
“Our little one was unlucky the most. He was bitten right between the eyes. So for three days he walked with his eyes closed, hand in hand with his grandmother. It’s good that the wasps didn’t get to the throat, otherwise I don’t know how Dimka could breathe ... "
Sasha, Tver
Consequences of wasp stings: from ordinary to the most severe
As noted above, the most characteristic and quite common consequences after a wasp sting are a slight swelling of the affected area and pain.The intensity of pain and the severity of edema largely depend on the location of the bite and how sensitive the victim is to insect venom.
Usually, after a few hours, severe itching joins the pain, and the soreness itself passes quite quickly, but the itching can last for several days, especially if the bite is constantly scratched.
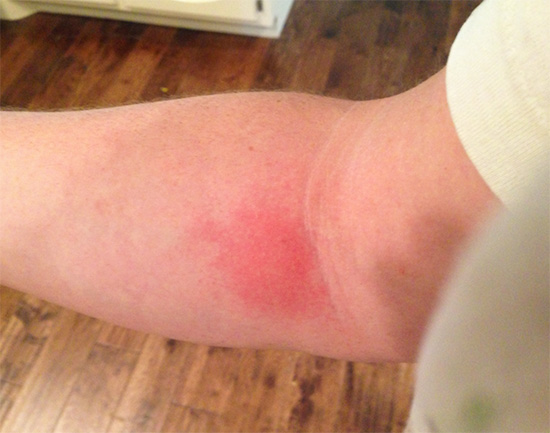
Inflammation after a wasp sting in unsensitized people is rarely extensive, but sometimes it also does not go away for a long time. If the bump stays on the body for more than two weeks, then you need to see a doctor.
Dangerous complications after a wasp sting can be due to various reasons, for example:
- if the attack of wasps on a person was massive and there were a lot of bites, then hemorrhages (subcutaneous hemorrhages) may appear on the body, with bites in the limbs, loss of their mobility and severe tremor are not uncommon;
- the victim may feel pain in the heart, dizziness, sometimes there is confusion due to a sharp decrease in blood pressure (and it does not matter whether the wasp stung in the chest or in the arm - the fact of a person's hypersensitivity to wasp venom is important);
- it can be very dangerous when a wasp bites in the throat or neck - swelling in this case can lead to blockage of the airways and asphyxia;
- a bite directly into the mucous membranes of the eye leads to severe inflammation, sometimes with subsequent suppuration and hemorrhages, an irreversible deterioration in vision of one degree or another is not excluded;
- a bite in the genital area is also dangerous - while urination causes severe pain, and in some cases, due to severe swelling, it becomes impossible at all.

Be that as it may, the main complications from wasp stings in most cases are associated with an allergic reaction.
Allergy to wasp stings
So, a wasp sting is dangerous, primarily due to the high allergenicity of the venom of this insect. Allergic consequences in this case can be either subtle or have a generalized form.
The usual response of the immune system of any person to a wasp sting is inflammation. Such a “response” of the body is necessary for the localization of toxins in the affected area and their rapid destruction by special cells of the immune system. However, inflammation is perhaps the most harmless consequence of a wasp attack.
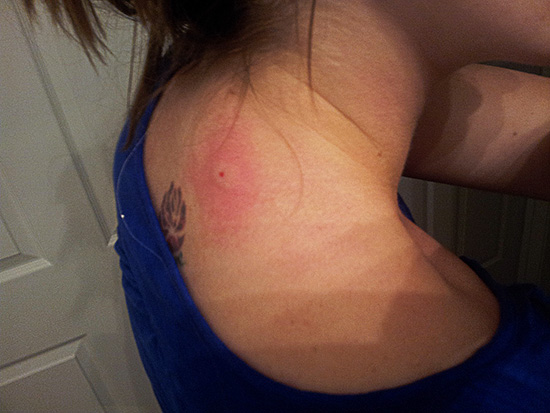
Other severe allergy symptoms are much more dangerous:
- Temperature. Even from a single wasp sting, it can rise to 39-40 ° C and occasionally higher. At temperatures up to 38 ° C, it is not worth knocking it down, since toxins are neutralized faster.
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain. They do not require gastric lavage or activated charcoal, but when they appear, it is advisable to refrain from eating.
- Quincke's edema is a very dangerous manifestation of an allergic reaction, sometimes leading to blockage of the airways. It occurs precisely in sensitized people (in victims with normal immunity, even in infants, such edema does not develop).
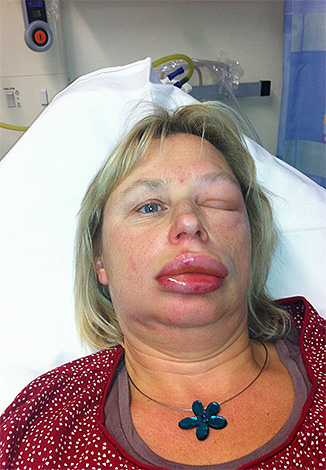
Important!
If there is a risk of blocking the airways during Quincke's edema, it is imperative to contact the doctors - at least by phone - to receive instructions on how to further help the person. It may turn out that in order to provide the victim with air, a conicotomy will be required - an incision in the throat area to install a tube that allows breathing.
- Anaphylactic shock is the most dangerous thing that can happen with a wasp sting, since in 10-15% of cases this condition ends in the death of a person.All previous symptoms can be harbingers of shock, and in addition to them, the victim's fingers turn blue during anaphylaxis, and acute pain in the chest appears. For adequate assistance, a person needs to call a doctor as soon as possible and get appropriate advice.
It should be borne in mind that sensitivity to wasp stings can develop gradually. With each new attack - regardless of the time interval between them - the body can react to a portion of the poison more and more sharply, and after a certain number of stings, any "meeting" with a wasp may already be fraught with a life-threatening allergic reaction.

In other words, in the case of the development of sensitization, the second, fifth, and twentieth bite can be extremely dangerous - everything is very individual here, and it is impossible to say specifically how many bites of wasps are fatal to humans.
On a note
Regarding the largest wasps - hornets - there is even a belief among the people that just nine bites are enough to cause death. According to legend, no matter how much time has passed between stings - a year or ten years - as soon as there are nine of them, a person will die. That is why hornets are sometimes called "nines".
Speaking about the danger of the consequences of wasp stings, one cannot fail to mention multiple bites - after all, even if a person is not allergic to poison, a simultaneous attack by several dozen insects can end in death for him. It should be borne in mind that, unlike bees, each wasp can sting repeatedly, since it does not leave its sting in the skin of the victim during the attack.
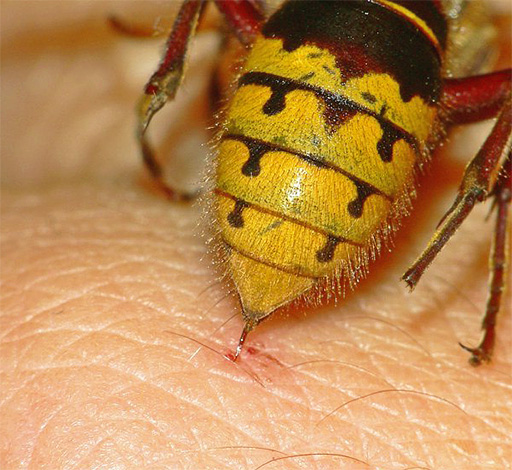

Generally speaking, the body of a healthy person (namely, his immune system) is able to quickly neutralize wasp venom, thereby reducing its harmful effects on tissues and organs. However, if a wasp attacked an allergic person, then it is categorically impossible to expect that his body will cope with toxins on its own: such a person must be given first aid, and at the first alarming symptoms, you should contact a doctor by phone for advice.
Allergies can develop very rapidly, and without prior first aid, irreparable things can happen during the time spent on the road to the hospital.
What to do with a wasp sting?
In order to minimize the effects of a wasp sting, the first thing to do is to try to suck out the poison from the wound (without spending more than 60 seconds after the insect attack), then treat the affected area with an antiseptic and apply a cold compress as soon as possible. Cold will narrow the blood vessels and reduce the penetration of the poison into the bloodstream - this is very important for allergy sufferers, since while the poison is localized, the negative effect it has on the body as a whole is minimal, and the active components of the poison continue to be continuously destroyed in the tissues.
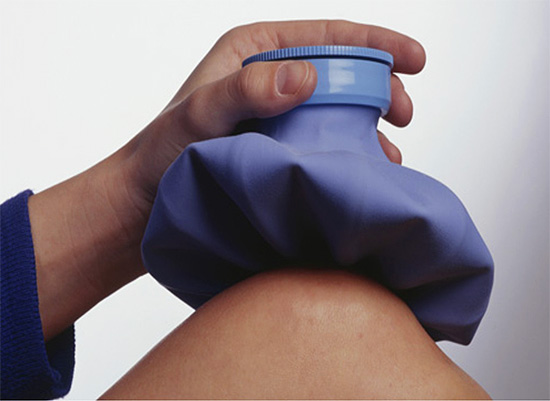
Subsequently, the affected area can be treated with Fenistil gel or Advantan ointment.
Review (from correspondence on the forum)
“Igor: Tell me, how long does a wasp sting last? On Saturday, that is, yesterday, I was bitten by one, so half my face was smashed, and tomorrow I have three presentations. I can't act like this in front of people. Are there any remedies to quickly remove this swelling?
Nemo: Go to the hospital, get a certificate and rest. The presentation doesn't work for you."
Further consequences of a bite can develop according to three scenarios, each of which requires the adoption of appropriate measures.
The first case is the most favorable: a small tumor remains at the site of the wasp sting, which itches or hurts, but the general condition of the bitten person is normal, he does not have a fever, there is no headache, the bite does not interfere with normal daily activities.
In this situation, it is recommended to treat the affected area with a suitable ointment or balm for insect bites. So the wasp sting will pass as quickly as possible. However, when choosing a remedy, you should always carefully read the instructions for it, because it may turn out that it is contraindicated for you.

So, for example, Advantan ointment has a hormonal effect, which excludes its use on large areas of the skin and delicate skin of babies up to 4 months old. Hydrocortisone ointment works in much the same way; but the drug "Fenistil" in this regard is considered the most versatile - it can be used even in children older than one month.
On a note
Remember that a wasp sting in any case will not pass earlier than 1-2 days. It is unlikely that a tumor can be completely removed before its normal natural disappearance.
The second scenario is the most common, although less pleasant: there are no severe allergy symptoms, but the pain at the bite site is quite strong, the swelling and swelling have spread to the surrounding tissues. The pain in this case may interfere with the person's normal work and rest, and the tumor may become too large.
In this case, the role of a cold compress is especially important. It can also be useful to treat the affected area of the body with an antihistamine or hormonal ointment - Fenistil-gel, Advantan, hydrocortisone ointment.All of them have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, inhibit the development of the tumor and relieve pain. It is desirable that the ointment be on the skin at the site of the bite constantly until the tumor subsides significantly.
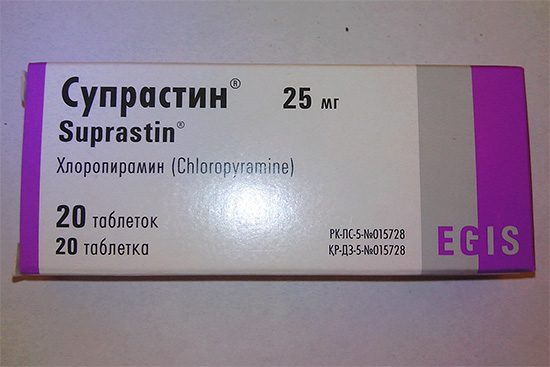
It is also necessary to consult a doctor (possible by phone) regarding the use of antihistamines in tablets (Suprastin, Diphenhydramine). If the pain syndrome is too pronounced, then you can additionally use Menovazin, as well as painkillers in tablets.
In this situation, the victim needs to drink as much as possible so that all the products of tissue damage are quickly removed from the body without leading to a deterioration in well-being.
And finally, the rarest, but also the most severe and dangerous case is the development of a severe allergic reaction. Often the situation first develops according to the second scenario, with rapid growth of the tumor and severe pain, and then more severe symptoms begin to appear. They can be different: headache, nausea, fever, rashes on the body, swelling in places remote from the bite site, allergic rhinitis, shortness of breath, asthma attacks, heart pain, sometimes diarrhea or vomiting.
The appearance of these symptoms is a signal to take emergency measures:
- As soon as possible, the victim needs to drink any systemic antihistamine - Suprastin, Tavegin, Kestin, Claritin, Diphenhydramine or their analogues (you need a doctor's consultation, at least by phone).
- The bite site should be lubricated with Advantan or hydrocortisone ointment;
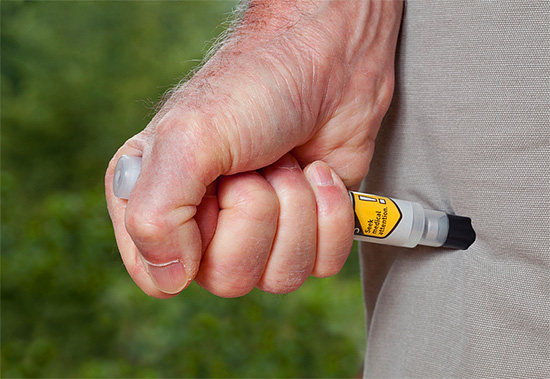
- If the victim is allergic and carries an autoinjector with adrenaline (epinephrine), then it should be used immediately after the bite, without even expecting any dangerous symptoms to appear;

- If the victim loses consciousness, impaired pulse and breathing, artificial respiration and indirect heart massage will be required;
- The victim is taken to the hospital as soon as possible.
It is important to understand that sometimes severe allergic reactions develop not just quickly, but at lightning speed. In the practice of many doctors, there were situations when a patient experienced anaphylactic shock before the doctor had time to pull out an ampoule of adrenaline from the box and inject it.
Therefore, at the first alarming symptoms, it is necessary to immediately begin transporting the bitten person to the doctor, so that in the most severe condition the person is already under the control of specialists. This is exactly the situation when a person's life can directly depend on your correct and timely actions.
A useful video about the possible consequences of wasp and bee stings, as well as first aid methods



Yesterday I was bitten by a wasp on the arm. To this day, the redness has not gone away. What to do?
Cry
I was stung by a wasp in the area of my left eye in November 2001. I did not go to the doctor, I was driving home after demobilization. In general, there was no emergency assistance. This bite made itself felt in June 2009. The same edema appeared in the same place. Now every year from June to November I have this "bite" appears. If you do not take a couple of suprastin tablets in a timely manner, then Quincke's edema is formed. What to do?
And once in the street toilet I was bitten by wasps, right behind the organ - the scrotum swelled up a little, it hurt, but that's okay.
Made me laugh, hahaha...
Yesterday an employee was buried from a wasp sting. He's allergic, instant Quincke's edema. I was at the dacha alone and did not have time to take the pills.
Five days ago, wasps bit me - they counted more than ten bites (including three in the head). Started to swell, called an ambulance. They injected suprastin, diphenhydramine and something else. The edema began to go down, the itching was for three days. Now, everything seems to be fine, but my head hurts a lot (pills do not help). Tell me, is this how it should be?
Yesterday the son-in-law was bitten by wasps. Quincke's edema, day 2 in intensive care…
When bitten, immediately attach a tomato (cut) and hold for 20 minutes. The swelling will disappear, the pain will go away in a day.
Apply gasoline or kerosene to the wound immediately after the bite. Right away, and not when 5 hours have already passed.