
Among all Asian insects, the Vespa Mandarinia hornet is one of the most famous. This is not surprising, if only because its huge size makes it extremely noticeable: a huge wasp with a body length of 5 cm and a wingspan of up to 6 cm somehow by itself attracts the attention of a tourist or traveler. No wonder in Asian countries this insect is also called a sparrow bee - for its impressive size.

However, the Asian hornet has another popular name - it is called a tiger bee for its extremely painful bites. Among local residents, in contrast to the rave reviews of tourists, the Vespa Mandarinia hornet has rather gained a bad reputation: its bite is deadly, especially for a person with hypersensitivity to insect venoms. If several giants attack at the same time, they can easily bite or cripple almost any person to death.
Among other things, the Asian giant hornet is a thunderstorm for all honey bees, so beekeepers in Thailand, India and Japan regularly suffer serious losses from the invasions of these predators.

It is interesting
The Vespa Mandarin hornet is one of 23 species of the hornet genus, which includes, among other things, ordinary European relatives. The size of this insect is just a simple anatomical adaptation to a hot climate (large-sized animals tolerate high temperatures more easily, since they have a large surface for heat transfer to the environment).In addition, due to its size, this giant can count on a large number of potential victims, even comparable in size to it. Otherwise, the huge Asian hornet is very similar to its other relatives.
As for the Russians, we are mainly interested in the Vespa Mandarin hornet as one of the dangers that can lie in wait while traveling in an exotic Asian region. Therefore, information about what the giant Asian hornet looks like, as well as how to avoid its bites, will never be superfluous.
Distinctive features of the tiger wasp
Asian killer hornets are generally similar in body shape and general color tones to ordinary hornets: they are also yellow with black stripes. However, individual color details still distinguish them from each other.

So, if the Vespa Crabro hornet, better known as the common European hornet, has rather thin black bandages on a yellow body and a dark red head, then the Vespa Mandarinia hornet is characterized by much thicker and more expressive black stripes on the body, as well as a yellow head.

Visually, it is the light-colored head with two large eyes that attracts the most attention.
The video shows Asian hornets caught in a sticky trap:
Giant Asian hornets caught in a sticky trap
Interestingly, the giant Vespa Mandarinia has three small accessory ocelli between the two main large eyes. These additional organs of vision help the hornet to distinguish between dark and light and navigate in space.
In the photo - Asian hornet full face. His extra eyes are clearly visible:


And yet, the main distinguishing feature of the giant hornet, which makes it possible to distinguish this insect from other relatives, is, of course, its size.With its spread wings, it almost covers the palm of a person, so at the first meeting it seems not quite real, but as if deliberately made unnaturally large. Such dimensions help the hornet in the first place to get food that is inaccessible to smaller relatives.
Lifestyle and nutrition of the giant Asian hornet
The Asian giant hornet leads the same lifestyle as all other members of the Vespa genus.
Hornets live in paper nests made from chewed pieces of young tree bark, held together with a sticky salivary secretion. The founding female gives birth to a new family, which at the beginning of the warm season simply lays a few eggs in the place where the nest will grow in the future.

At first, the female herself obtains food for the larvae, takes care and cares for them. However, already a month after the eggs are laid, young hornets are hatched from them, which, in turn, take care of feeding new larvae and protecting the family. The uterus, on the other hand, greatly limits its role - until the end of its life, it continues only to lay eggs.
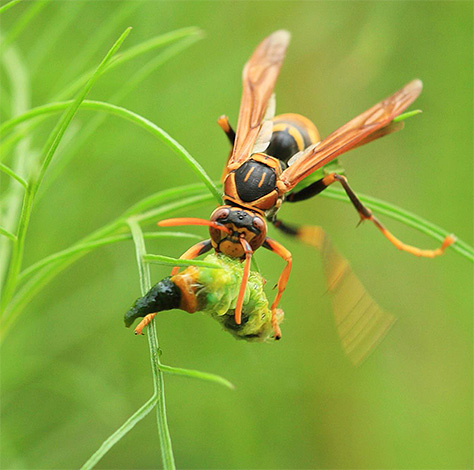
In nutrition, the Vespa Mandarinia hornet is picky: the basis of its diet is a wide variety of insects. A huge Asian hornet will also not mind eating meat or fish washed ashore, fruits and berries. Unlike adults, the larvae feed exclusively on animal food, however, this feature is also characteristic of all other hornets of the Vespa genus.

It is interesting
Hornets almost never use their poisonous sting to get food. They kill other insects with powerful jaws, which literally crumble the chitinous covers of their victims.
The largest hornet in the world is widely distributed: it is found throughout Southeast Asia and reaches the Russian Primorye, where it is quite common and numerous.
It is worth noting that the Vespa Mandarinia species is divided into several subspecies at different points in its range. So, in Japan, for example, there is a subspecies of the Japanese huge hornet, endemic only for island territories.

In general, hornets of this species are common in different biotopes, but most of all they prefer forests and various light groves. Thus, it will not work to meet the Asian hornet in the highlands, steppe and desert areas.
Vespa Mandarinia poison and its effect on humans
The Asian giant hornet is very poisonous: its poison is considered one of the most toxic among all insects in general. However, due to the fact that this huge predator, when bitten, does not introduce the entire supply of poison into the wound, in general, the bite of the Asian hornet, although extremely painful, does not pose a mortal danger to a healthy person with a normally functioning immune system.
On a note
Every year in Japan about 40 people die from the bites of giant hornets. Thus, the hornets here set a kind of anti-record - no other wild animal can "boast" of such indicators.
Photo of the sting of the Asian hornet:
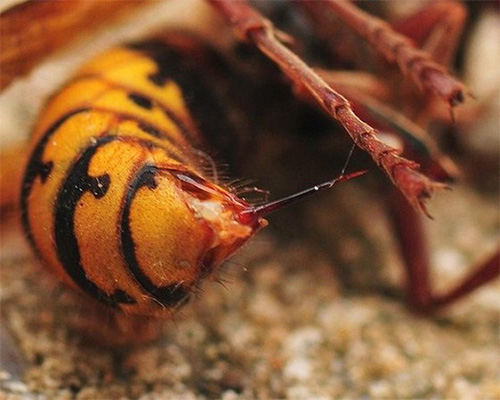

Due to the presence of several protein toxins in the hornet venom, its entry into soft tissues immediately activates cell lysis, which is accompanied by instant swelling and inflammation. The presence of histamine and acetylcholine in the poison - substances that ensure the occurrence of an immediate immune response and the transmission of neuromuscular reactions - causes a sharp pain effect, sometimes accompanied by a state of shock in the victim.
Review
“After being bitten by a hornet, I was in the hospital for three weeks. I had a huge swelling on the whole side, I could not move my arm. The bite itself is simply monstrous - as if a drill is drilled into the body with an ordinary drill. When the insect bit me, I barely had time to reach the house and lost consciousness. The wife has already called the medics. And one of my friends died a year ago from a hornet attack.
Tai Won Xing, Jilin
Quite a typical response of the body to a hornet bite is considered to be extensive tissue edema, which was already mentioned above, increased heart rate, headaches and fever.
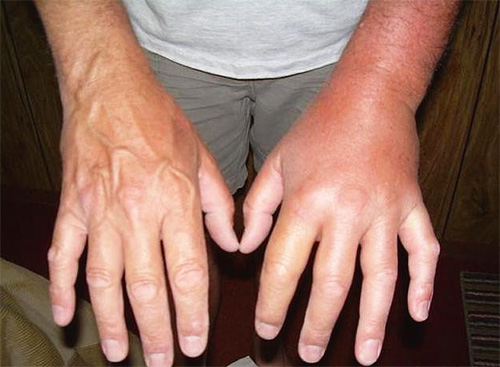
However, in people sensitive to insect toxins, even a single bite from a giant hornet can cause anaphylactic shock and death. If there were numerous bites, then in this case, even for a healthy person, the attack is fraught with tissue necrosis, extensive hemorrhages and damage to internal organs.
Reproduction of giant hornets
Now let's look at how the Vespa Mandarinia hornet continues the genus. There are several key points here.
- The family of giant hornets exists for no more than one year.
- When the housing of these huge wasps grows to a decent size, and the working individuals themselves become quite numerous, the uterus begins to lay eggs, from which males and females capable of breeding are hatched.
- At a certain point, these sexually mature individuals swarm and mate, after which the young males die, and the females seek secluded shelters for themselves and remain in them until spring.
- By the rainy season (and in the Primorye region - by winter), the old family dies out completely, since the uterus stops laying new eggs.
It is worth noting that sometimes all Vespa hornets do not live up to the time of natural death, as they die from ticks or infections.
A disaster for man or an adornment of nature?
In a global sense, giant Asian hornets are, of course, dangerous to people, but this danger is not critical, since it is entirely and completely provoked by the person himself. These insects are not very aggressive by nature and will only attack in self-defense or nest defense.

Hornets do much more harm to apiaries, especially those that breed less aggressive European honey bees. Sometimes hornets have time to destroy an entire bee family in a few hours, and therefore local beekeepers wage an ongoing systematic struggle with them.

In general, mortality from giant hornet bites is quite high: in some regions, up to 100 people die per year. But in fairness, it should be said that most of the dead are the same beekeepers who, without special means of protection, actively destroy hornet nests and, as a result, fall under their massive attacks.
A simple tourist who accidentally finds himself in the forest next to the Vespa Mandarinia hornet should not be afraid of this insect - it will not attack without a reason.
On a note
In the West, synthetic substances are added to many dietary supplements, similar to the secret contained in the developing hornet larvae. It is believed that these components increase a person's stamina. However, there is no experimental evidence for these claims.
In conclusion, it should be noted that for wildlife, giant hornets are one of the most active natural orderlies.They successfully destroy many pests of forests and agriculture, therefore, in most biocenoses - including on agricultural lands - they are useful and deserve protection.
Several dozen hornets completely destroyed the bee hive



