
Wasp venom is similar in composition to bee venom. In addition, many bitten people cannot even unambiguously say whether the wasp stung them or the bee - the effects of the poison on the affected tissues are so similar.

Today, scientists have managed to study the composition of both bee and wasp venom quite well. At the same time, an important distinguishing feature was established: wasp venom is somewhat more allergenic and often leads to complications in the form of various manifestations of dangerous allergic reactions (for example, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock). However, one should not think that from this point of view, bee venom is harmless - it is also "much" for this, just with a slightly lesser probability.
Partly for this reason, "reproach" is generally not known as a method of traditional medicine. Despite the fact that bee stinging is a fairly common and widely known procedure.

On a note
Among experts, there is an opinion that the notorious apitherapy and the benefits of bee venom are nothing more than a marketing ploy for beekeepers who need to sell the excess of their products.Not a single serious study has confirmed, for example, the benefits of bee stinging, just as the healing properties of other methods of apitherapy have not been proven.
With a high probability, the benefits of propolis, wax moth, royal jelly and bee venom are nothing more than a placebo effect, and these beekeeping products are widely used precisely because of their availability: they can be obtained in apiaries in almost any quantity.
But it is extremely difficult to get wasp venom, because no one specifically breeds them, and for the drug you need to climb into the nest of wild wasps. And this is another explanation why, despite the similarity of the compositions, the poisons of these closely related insects vary so much in popularity in traditional medicine.
As a result, even doctors and toxicologists cannot always say unequivocally today whether wasp venom is good for humans. Its composition really contains stimulating and tonic components, substances that stimulate metabolism, but it is not rational to isolate them from the poison - today there are many much safer analogues of both natural and synthetic origin on the market.

But due to the large number of harmful and allergenic components, it can be very dangerous to use unprepared wasp venom for treatment.
The composition of wasp venom and the effect of its components on the human body
In the overwhelming majority of cases, wasps use their sting primarily for self-defense, and only in rare cases - to kill larger and too aggressive prey. Therefore, as a rule, the main goal of a wasp sting is to cause severe pain in the victim and scare him away.
The composition of wasp venom includes a set of substances that strongly act on nerve endings and cause a rapid immune response of the body.Among the main components, the following components can be distinguished:
- Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter involved in the conduction of nerve impulses. At high concentrations, it disrupts the functioning of the nervous tissue, blocking the transmission of excitation along the nerve fibers.
- Histamine is the main activator of inflammation and allergic reactions. Its action can lead to a variety of manifestations: there is itching and swelling at the site of the bite, and especially sensitive people develop urticaria, fever, in rare cases, anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema.

- Phospholipases are special enzymes whose task is to destroy cell walls, which leads to the release of contents from cells into surrounding tissues and provokes an inflammatory process. For the victim, this means pain at the site of the bite, which he will feel while the inflammation lasts. In addition, phospholipases contribute to the destruction of the walls of mast cells, due to which additional amounts of histamine are released into the blood and an allergic reaction intensifies.
- Hyaluronidase is a toxin whose action is similar to that of phospholipases.
- Hyperglycemic factor that increases blood sugar levels.
In hornets, the composition of the poison also includes specific mastoparana toxins, which have a powerful destructive effect on cells.

Review
“I had one time that a hornet stung. I got used to bee stings in the apiary, they don’t bother me at all, I boldly catch and crush philanthropists. But the hornet vandalized so that it already darkened in the eyes. Well, I had all the evidence closed. I just got to the trailer, lay down to lie down. The pain was hellish, my heart was seized, I just thought that I would put a cold one on my hand.It blew her up nicely, to the very shoulder, it itched a lot. A neighbor in the apiary offered to take me to the hospital, but nothing happened. The next day, only the itching remained, and then gradually the swelling began to subside.”
Mikhail, Semipalatinsk
The effects of wasp venom on the human body
Now let's see how wasp venom works, so to speak, at the macro level, that is, what symptoms occur.
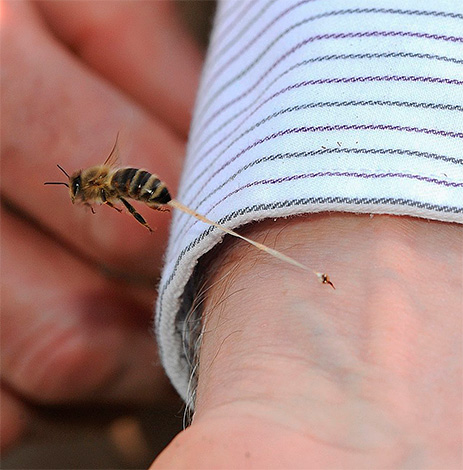
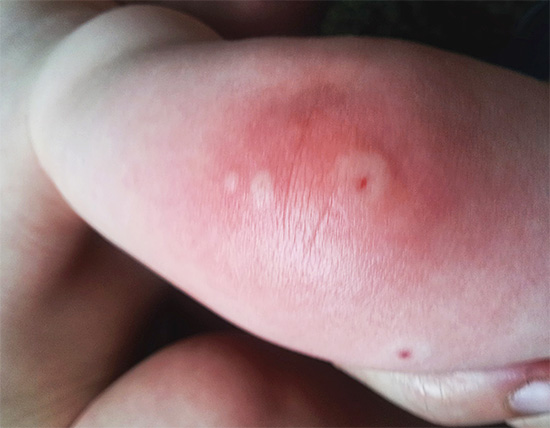
At the moment of sting, the effect of the poison injected under the skin causes a sharp pain, and almost immediately leads to the appearance of a small pale edema at the site of the bite. After a few minutes, the bite swells more, it may turn red, it becomes hard, and a feeling of severe itching appears on the skin in its area. At this time, the first symptoms of allergies may appear - hives, fever, shortness of breath, headache, confusion.

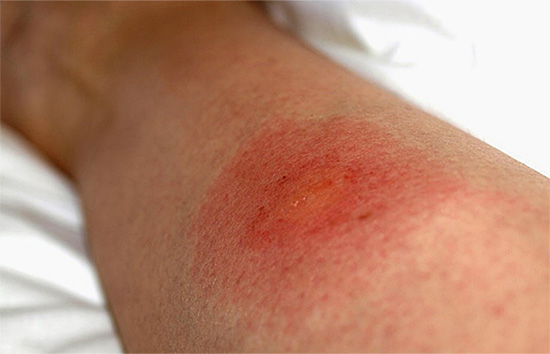
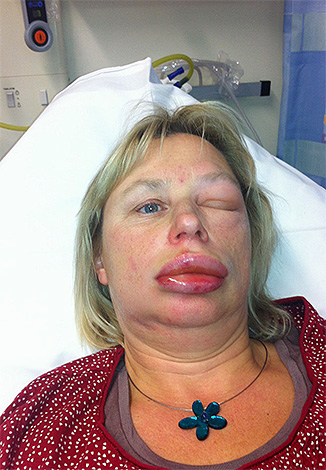
The most severe consequence of a wasp sting is anaphylactic shock - an extreme degree of an allergic reaction. It occurs rarely and only in people who are hypersensitive to the poisons of hymenoptera insects. But it is precisely because of anaphylactic shock that the number of deaths from wasp and hornet stings is so high. Such a reaction develops very quickly, literally within a few minutes after the bite, and sometimes the victim does not even have time to be taken to the hospital.

By and large, the benefits of wasp venom, even if there is one, are completely offset by the risk of a dangerous allergic reaction (especially when you consider that with each subsequent bite, the body's sensitivity to poison may increase).
Review
“People are regularly brought to our hospital who are attacked by huge hornets.There are many beekeeping farms in the area, and hornets actively populate all the surrounding forests, as they constantly fight with bees. Usually, after a bite, the patient develops a severe allergy, which is limited to swelling and rashes on the skin, the temperature may rise and pain in the head may appear. But sometimes there are severe cases, with hemorrhages, swelling of the larynx and anaphylaxis. Last year, for example, there were two deaths, and in one, a 12-year-old girl died.”
Naomi Kurosaki, Saito

But after special processing in the laboratory, wasp venom can become much safer and more useful.
The use of wasp venom in medicine
It is for allergy sufferers, in whom wasp stings lead to serious consequences, that special vaccines are prepared on the basis of wasp venom. They reduce the titer of histamine and some toxins, but retain the original amount of specific components by which the human immune system can identify the poison.
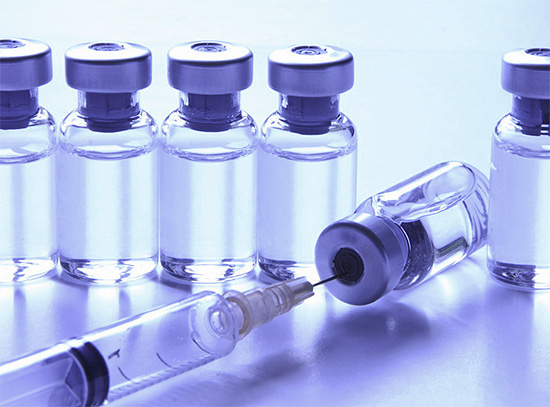
Before the warm season of the year, when there is a possibility of being stung, the patient is vaccinated to develop a normal immune response to the bite. As a result, after a chance meeting with a wasp, the reaction to a sting in a person will be much less pronounced and not so life-threatening.
Wasp venom can also be useful due to the actual toxins that make up its composition. So, for example, in Barcelona, the development of a method for combating cancerous tumors based on the defeat of cancer cells with the biological components of wasp venom has already begun quite a long time ago.

Scientists are trying to combine toxin molecules with transport protein molecules that will carry the poison directly to cancer cells without affecting healthy ones.In mice, such a drug has already proven its effectiveness, and work is currently underway to study its effect on human tissues.
The most poisonous wasps in the world
Although all wasps are poisonous, the strength of the poison and the consequences of bites vary from one type of wasp to another. In different representatives of the suborder, the ratio of the components of the poison can vary greatly, and many of them have unique components in the poison that have a specific effect on the victim.
So, for example, the bite of road wasps of the genus Pepsis is the most painful. Most representatives of this genus specialize in the extraction of tarantulas for their larvae. Their sting is considered one of the most painful insects in the world, second only to that of the South American Paraponera clavata ant.


The bite of a huge hornet (Vespa Mandarinia), which lives in Southeast Asia and Japan, is statistically the most dangerous among wasp representatives. Every year, about 40 people die from the attacks of these insects in Japan alone, and the number of victims in the entire habitat of these hornets exceeds a hundred.

The composition of the poison of a huge hornet differs little from the composition of the poison of the European hornet, but in one bite the insect introduces a much larger dose of toxins into the human body. In addition, when attacking, the hornet can make several stings at once with a short interval, which often leads to hemorrhages and extensive edema in the future. We can say that the huge hornet is the most poisonous wasp in the world.
But the scolia wasps, despite their truly gigantic size, sting rather weakly. Their venom is designed to paralyze prey, not to scare off the enemy, and therefore entomologists boldly catch these large black wasps with their bare hands.
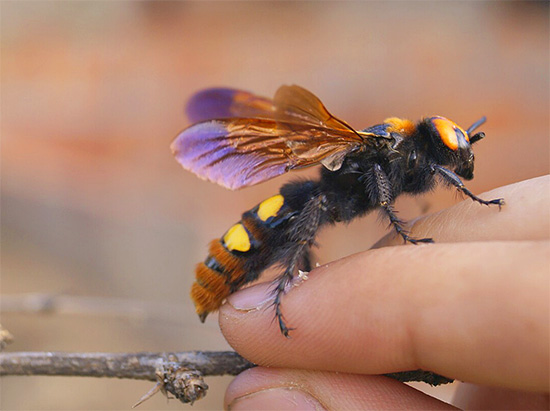

Very painful wasps sting and German wasps.The females of the latter are easily confused with ants due to the fact that they lack wings. These insects are parasites in the nests of other wasps, and it is thanks to their strong poison that they can even defend themselves against hornets by penetrating into their nest.


And in conclusion, we note once again: it’s still not worth counting on wasp venom to be useful for the body. In case of accidental sting, this, of course, could be a small consolation, but you should not specifically catch wasps and apply to the body, because even the possible positive effects of a bite will be blocked by severe pain, unpleasant swelling and the risk of developing a dangerous allergic reaction.
Useful video: what to do with the development of a dangerous allergic reaction to wasp and bee stings





When a wasp or bee stings, honey is an effective remedy. It is necessary to smear the bite site and take it inside.One tablespoon is enough. It relieves all symptoms, it also has a very positive effect on allergy sufferers (poison weaved and wasps). If there is an allergy to honey itself, then it is enough to coat the bite site.
The article says that the benefits of bee stinging have not been proven by science and this is a marketing ploy for beekeepers to better sell their products. Well, then let the author explain why professional beekeepers live up to 90 years or more, and what this is connected with. Could it be that they are constantly stinged by bees, and then they get used to it and do not even pay attention to it.
It's from the honey, not the poison.
Every year in the fall I put out the bait, catch wasps and apply it to the joints.
What kind of nonsense you wrote, apparently stupid.
I'll tell my story. I am now 53 years old, all my life I have not been able to eat any fish, even when they cooked fish at home or, God forbid, I caught a poorly washed dish somewhere after the fish, then things could come to death. I tried 2 times in my life to try fish with a meager piece - it came to an ambulance with pumping me out. Doctors strictly forbade even close to the fish to come up.
And so 1 year ago I went to the forest for mushrooms on the Karelian Isthmus, and it so happened that crossing the forest river along a fallen tree, I disturbed the forest wasps. It was hell! A cloud appeared in front of me, as if the night had come, and then it began. I don't know how I "flew" over this log, threw the basket. Result: the hands were like those of a drug addict, the neck became a stake. I was saved by the fact that I take 1 tablet of Dexamethasone per day for kidney disease.
So, about a month has passed and I noticed that I don’t react when they cook fish.And then I decided to try a small piece of fish. So what? Now I eat like a normal person! I think thanks to the wasps - yes, it was hell, but it was worth it. Medicine was powerless, but the wasps were cured!
The article is biased, there are many weak points. But for the layman will go.
Actually, I saw a Japanese hornet and made friends with it. He didn't sting me, so here... A wasp also flew to me. Then she sat down on the cupcake, then passed into my arms. The wasp didn't even sting me. Ufff.
However, I decided to domesticate the wasp. I named it Threat. From today, the Threat lives with me. By the way, my hornet is also already domesticated. I named the hornet Bandit, because of the nature.