
The cabbage moth is a widespread pest worldwide. This butterfly is known for the fact that its caterpillars are able to bring a head of cabbage into a form that cannot be stored with just a few gnaws - because of the holes gnawed in the leaves, the cabbage begins to deteriorate quite quickly, and can be stored for no more than a few weeks.
At the same time, the cabbage moth itself is quite unsightly in appearance, and does not catch the eye of gardeners. However, being so inconspicuous in the fields, it constantly keeps agronomists in good shape, as its caterpillars are able to quickly develop on wild rapeseed and colza along the borders of the fields, and constantly threaten to cause serious damage to the entire crop. That is why the fight against cabbage moth continues from year to year, and over time it becomes more and more fierce.
Description of the pest: appearance and characteristics
The cabbage moth belongs to the family of ermine moths. These butterflies are known for having a slender, elongated body, and some types of ermine moths are brightly and contrastingly colored.

However, this does not apply to cabbage moths. She is a butterfly with a discreet, patronizing color.Its wings are a neat light brown color, with a light pattern in the center. When a butterfly is resting on a plant, it looks like a small straw when viewed from above.
Butterfly wings are about 7-8 mm long. The cabbage moth is an unimportant flyer, and, as a rule, the butterfly does not fly far from the place of exit from the chrysalis. Its wings have a beautiful fringe along the edges, and at the ends, in a calm state of the insect, they are slightly lifted up. The photo below shows a butterfly when viewed from above:
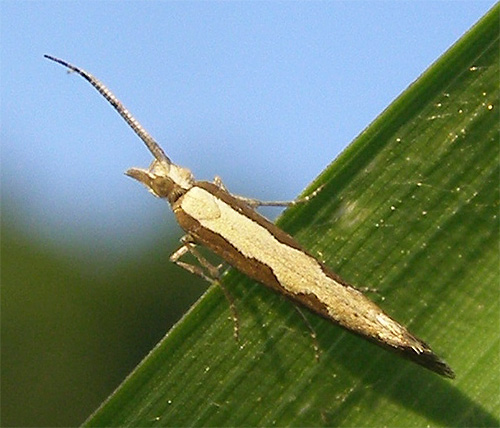

and below is the same, only on the side:

But the caterpillar of the cabbage moth is painted in a pale green color. Her body is covered with fine hairs, her head is almost brown. Caterpillars are rarely found in large clusters, as a rule, one or two larvae are present on one plant.
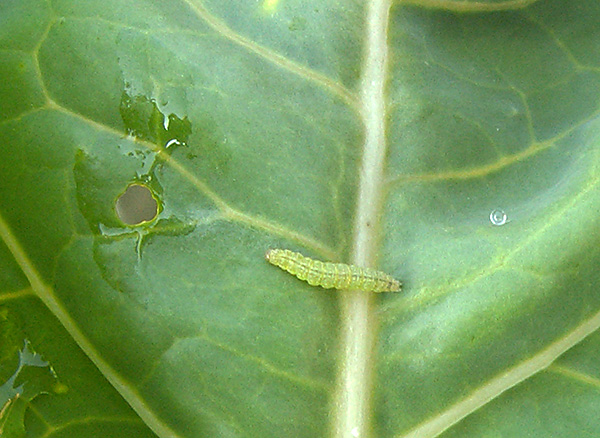
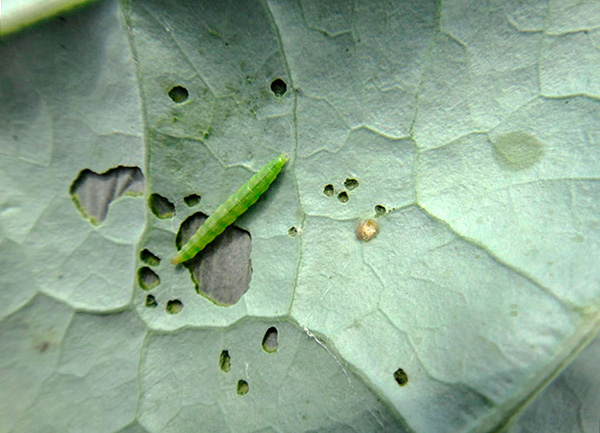


The eggs of the cabbage moth are small and elongated, reaching a length of 0.44 mm and a width of 0.26 mm. The color of the eggs is green, like the fodder plant itself.
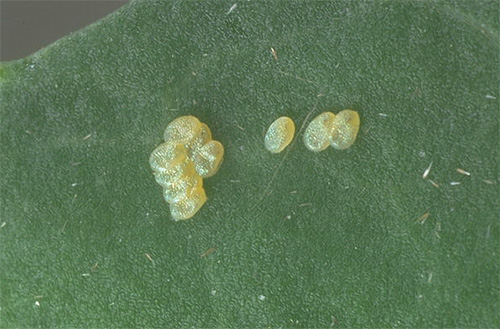
The pupa of the cabbage moth is dark yellow in color and is usually found on the stems and leaves of the plant.
Lifestyle, nutrition and reproduction of the cabbage moth
The cabbage moth is widely distributed throughout the world. Its homeland is Southern Europe, and initially the pest's habitat was limited to areas where winter frosts destroyed pupae and adult butterflies.
However, today the cabbage moth is actively conquering even the agricultural lands of the Murmansk region, successfully wintering in mulch and among unharvested grass, and with the cabbage itself it has managed to spread across America, Asia and Africa. Moreover, some cultures in Australia, New Zealand and the Hawaiian Islands are seriously affected by this butterfly. She can be recognized as a real cosmopolitan.


It is interesting
The conquest of the world by the cabbage moth was swift and somewhat like the victorious procession of the Colorado potato beetle through the potato beds of the Old World, only in the opposite direction. In 1854, the butterfly was first recorded in Illinois, and at the beginning of the last century it successfully crossed the Rocky Mountain range and found itself in British Columbia.
The cabbage moth is famous for its speed of reproduction. Its eggs develop in 2-3 days, the caterpillars manage to fatten up in one and a half to two weeks, the development of the pupa continues for another week or two. As a result, in the North, moths give 1-2 generations per summer, in central Russia and Europe - 3, in the Southern regions (Krasnodar, Stavropol Territories) - 4 generations, and in the south of Kazakhstan, in Ukraine and in Transcaucasia - up to 6 generations per summer. one warm season.
On a note
At temperatures below plus 4 ° C, the caterpillars and eggs of the cabbage moth die.
Pupae and adults overwinter in the pest.
One female lays up to 165 eggs in her life, but at the same time, in each clutch she has no more than 4 eggs, usually 2-3. This distribution reduces the death of eggs from predators and parasites.
An adult butterfly feeds on the nectar of flowers, and the caterpillar feeds exclusively on the tissues of the leaves of host plants. Actually, this is how it harms the crop.
Butterfly harm and signs of its appearance on the site
Small caterpillars that have just hatched from eggs immediately gnaw through the outer shell of the plant leaf and for the first time feed inside it, forming mines. After reaching a certain size, the larvae come to the surface of the leaf and continue to feed on its tissues, leaving only a thin outer shell on the other side.


Cabbage moth caterpillars can feed on almost any cruciferous plants - all varieties of cabbage, radish, radish, swede, turnip, rapeseed, mustard.
Caterpillars cause the greatest harm to cruciferous plantings in the hottest period of summer, reducing the assimilating ability of leaves and increasing the number of leaf burns. On young plants, caterpillars actively gnaw buds and buds, which reduces the total number of ovaries on the plant.
External signs of the appearance of moths on the site are numerous:
- noticeable damage to the outer and rosette leaves of cruciferous
- the appearance of gnawed buds and damaged young heads on cabbage
- mines visible in the light in the leaves
- the caterpillars themselves.
Often a good sign of a moth attack on a cabbage bush is the rapid drying of the outer leaves of the cabbage head or the stunting of the head as a whole.

This is due to damage to the base by its larva.
Ways to deal with cabbage moth
Measures to combat the cabbage moth are numerous and should be applied in combination. Among them:
- Careful plowing of crop residues and green manure plants. It is on them that a large number of pupae remain to winter. Butterflies cannot get out of the ground in spring.
- Weed control, especially near plots. They are often breeding grounds for pests.

- If more than 10% of plants are damaged or more than 4 caterpillars are found on one bush, the bushes are treated with insecticides.
On a note
The cabbage moth has a huge number of enemies, not counting just enemies like birds, lizards and toads. Many riders and wasps lay their eggs in the body of the caterpillars of this butterfly, and their larvae destroy the caterpillar itself, preventing it from pupating.Sometimes such parasites destroy up to 90% of moth caterpillars and pupae. Today, biological methods of combating moths with the help of such helper insects are being actively developed.
However, cabbage moths have been familiar with insecticides for a very long time, and therefore their use is less and less effective.
Means for the destruction of the pest
The cabbage moth was the first agricultural pest to develop resistance to Entobacterin, a drug based on pathogenic bacteria for moths. A little later, a population of cabbage scoops was discovered, which was also resistant to this agent.
It is interesting
Back in the 1980s, the cabbage moth developed resistance to pyrethroids and pyrethrins, and a few years later, scientists found populations of these moths resistant to most insecticides used in agriculture.
However, totally resistant moth populations are rare. Therefore, Entobacterin, Bitoxibacillin, Lepidocid, as well as products based on pyrethroids and pyrethrins, can be used against the pest in the gardens themselves.
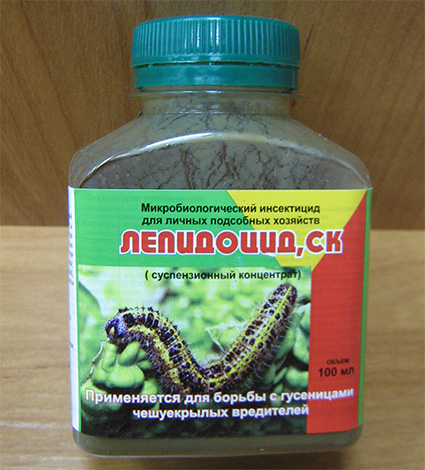


Only if the use of a particular drug does not give an obvious result, you should switch to another. Most likely, already on the first attempts, a remedy will be found that can destroy the mole.
It is important to remember that it was the widespread and thoughtless use of insecticides that hardened the moth and contributed to the development of resistance in it. Therefore, in the fight against the pest, in the first place, agrotechnical methods should be used, and only supplement them with poisons.





Not only did they eat all the white mustard, then they switched to cabbage, they also took a fancy to the tomatoes. Appetite grows 🙁
What plants should be planted near the cabbage to scare away the cabbage moth?
I don’t know how true it is, but they say that you need to sprinkle with a solution of mustard powder.
When dealing with these pests, the beds should be treated with a solution of mustard, salt and black pepper. The composition is prepared as follows: for 10 liters of water, two tablespoons of mustard are taken, then 2 the same tablespoons of salt and 1 teaspoon of pepper.