
When leaf-cutting ants first caught the eye of scientists, they thought the insects were picking up bits of leaves to hide in an anthill and feed on them. At the same time, even the mechanism of cutting leaves and their transportation was charmingly interesting and has already attracted the attention of a large number of specialists.
But then it turned out that this was only the beginning of a huge and complex process of processing and using leaves as raw materials for a real farm. And so complex that a small leaf-cutting ant became a real sensation in science for a long time ...
General description of leaf cutter ants
Leaf cutter ants are not outwardly remarkable. They have a small brown body - from 5 to 20 mm, depending on the caste - and long legs, especially characteristic of ants that often move through trees.


It is interesting
In the anthill of leaf cutters, there are 7 castes of these ants, which perform 29 different functions.
A distinctive external feature of the leaf-cutting ant is its powerful hooked jaws, with which it gnaws rather hard leaves of tropical trees.

All castes have these jaws, including the uterus.Powerful muscles are required to move them, so the head of the leaf cutters is also quite large.
The video shows how leaf-cutting ants gnaw off a green leaf.
Video: leaf cutter ants gnaw off a piece of leaf
Noteworthy is the difference in size between different castes of leaf-cutting ants. Those individuals who are busy in the anthill caring for eggs, farms and the uterus are small - only about 5-6 mm in length reaches their body. But their soldiers are huge. Compared to the "home" caste, these are real tanks: they can exceed the length of worker ants by 3-4 times, and by weight - several tens of times. Their uterus is even larger and sometimes weighs 700 times more than the smallest members of the colony!

It is interesting
Not every anthill at the leaf cutters has its own soldiers. Only very powerful colonies, numbering more than half a million individuals, can afford such a luxury: a smaller family simply cannot feed its defenders.
The uterus of all leaf cutters is very different from other individuals with a very powerful and large chest. Before mating, she has wings, but after the summer she bites them off for herself and proceeds to form a new colony. And this is where the fun begins...
Agricultural activity of leaf cutter ants
Leaf cutter ants do not need leaves for direct eating: these insects cannot absorb hard plant fibers. Therefore, the leaves are carefully chewed by a special caste of ants, after which the mass mixed with saliva is stored in chambers in which a constant microclimate is maintained and infected with a special fungus. It is this fungus that is the food for both adult ants and larvae.

Not surprisingly, leaf cutter ants have another name: mushroom ants. At the same time, the ants themselves do not eat the fruiting bodies of the mushrooms - only the mycelium is suitable for food, sprawling like a cobweb in the thickness of the forage mass and above it. Fruiting bodies are an extra waste of resources of the mycelium, and insects caring for the farm bite them even at the stage of setting.
On a note
The saliva of leaf-cutting ants contains several antibiotics that destroy parasitic fungi and bacteria that can destroy the main mycelium. But ants also have allied bacteria - special actinobacteria that suppress the development of a parasitic fungus on the mycelium.
In general, the ant and the mushroom "found each other" for a long time: today there are almost 200 species of ants in the world that grow mushrooms in one way or another. Some ants grow mushrooms in the anthill on dead insects and feces, but these species are considered the most primitive. But leaf cutters have adapted to use the most affordable and easy-to-process plant material as a raw material for the farm.

It is interesting
Leaf-cutting ants in their habitats are considered serious pests: a large anthill can literally cut several trees in the area naked. Therefore, on the farms of Venezuela, Colombia and Brazil, they diligently fight with the advent of leaf cutters.
The device of an anthill of small mushroom growers
Although leaf-cutting ants are tied rigidly to trees as sources of leaves, they equip their anthills almost exclusively underground.It is quite simple to explain this: only under a layer of earth are they protected from temperature extremes, to which mushrooms are very sensitive, and from excessive exposure to moisture.

The anthill itself in a vertical section looks like a huge egg. In the very center of it, farthest from any dangerous factors, there is a chamber with a uterus. It is surrounded by incubators in which eggs and larvae develop. All outer chambers are farms where ants grow mushrooms. As some researchers note, the analogy with the egg here is not only figurative, but also functional - in the center of it is the main reproductive organ, and on the periphery - food supplies.
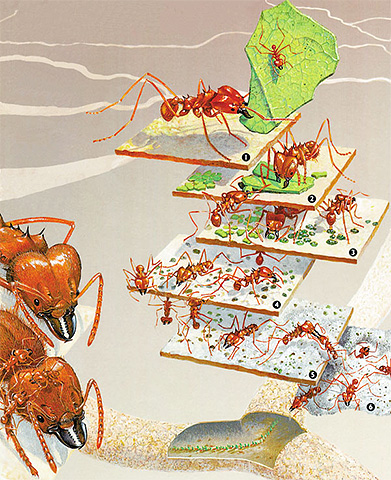
Up to several million individuals can live in a colony of leaf-cutting ants, and the entire anthill can be several meters in size.
Some leaf cutters make piles like those organized by our wood ants. But the heart of the anthill still remains underground.
It is interesting
Some types of leaf-cutting ants take out the garbage from the anthill, while others store it in special garbage chambers.
In addition to humans, leaf-cutting ants have only one serious enemy - one species of nomadic ants, which practically do not run out to the surface, attacks leaf-cutting anthills and ruins them, eating both ants, their brood, and mushrooms.
Reproduction of leaf cutter ants
Leaf cutter ants reproduce similarly to other species. At a certain point in the life of the anthill, usually tied to the season of the year, worker ants feed the larvae with the addition of special substances that stimulate the development of sexual individuals.Males and females capable of reproduction have wings, and when their number in the anthill reaches a certain critical value, they fly out, swarm and mate.
It is interesting
In some species of leaf cutter ants, worker ants can lay eggs if the queen dies. In some species, males incapable of reproduction emerge from such eggs, in others, normal individuals. The salvation of such an anthill will be a fertilized female who happens to be nearby, seeking shelter. But such encounters are extremely rare. Polygyny, the presence of several queens in an anthill, is not characteristic of leaf cutters.
In swarming, each female mates with several males to collect enough seed.
After swarming, which usually lasts one day, males and females scatter around the anthill. Males die, and each female digs a hole 30 cm deep in a convenient place and begins to lay eggs. Immediately, she folds several found and chewed leaves, which she infects with a piece of mycelium.
The female feeds the first larvae with the trophic eggs laid by her and a new mycelium. She herself does not eat at this time and survives due to her fat reserves and gnawed off wings. For 40-60 days, the first working individuals are hatched from her, which begin to perform all the “routine” operations for her.

It is interesting
On the lower part of the head, the uterus has a special pocket in which it puts a piece of mycelium before leaving the parental anthill. It is this stock that will ensure the normal development of the farm in the future.
Leaf cutter ant larvae are unable to feed on their own, and adult ants feed them on fungal hyphae.
Despite such a complex social structure, leaf-cutting ants, although with certain difficulties, may well be kept in captivity. For example, you can look at a large anthill in the insectarium of the Moscow Zoo, where birch and rose leaves are specially frozen for ants for the winter. Yes, and many amateurs manage to successfully grow leaf-cutting ants at home. In general, leaf-cutting ants are exclusively residents of the tropics of South America and several Caribbean islands. Their relatives have not yet been able to adapt to the temperate climate.




It was very interesting to read that tiny ants, it turns out, are able to grow mushrooms! And in general, your site is very informative, when I came here for the first time, I just lost my speech)) Very pleasant colors, beautiful pictures and all the information is clearly and accessible.
I went in for the first time, read the title - and I had to read the article incessantly. Informative though)
And I liked the article.
Very interesting! First time and love it! Thank you.