
According to statistics, about 30-50% of urban apartments are inhabited by dust mites, which are the cause of many cases of allergies. Studies have shown that respiratory diseases of unknown etiology (including asthma) are also often caused by house dust, which often contains waste products of insects and arachnids, which are strong allergens for many people.
It may seem surprising, but even in a seemingly clean room, hundreds of thousands of dust mites can live. They are very small (not visible to the naked eye), do not bite a person and do not attract attention in any way. At the same time, people indoors can suffer for years from constant runny noses, conjunctivitis, dermatitis, allergies, and they cannot find the cause of the disease. While the danger sometimes hides very close - literally under the pillow ...
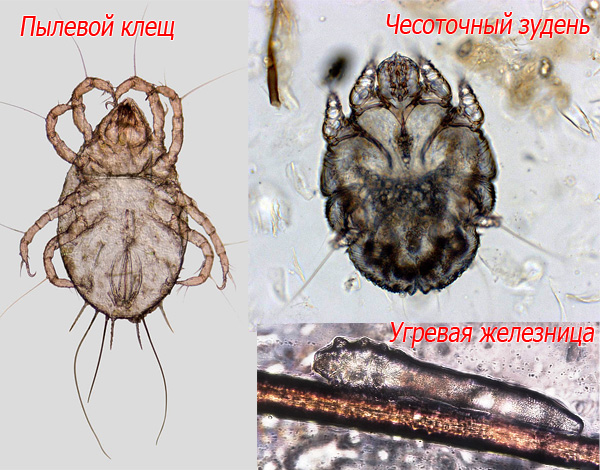
General view: who are dust mites?
Dust mites are small arthropods of the order of acariform mites that live in private houses and apartments and feed mainly on exfoliating dry skin and human hair.

These creatures do not bite a person, do not suck his blood, and do not even gnaw the skin directly on the body. All their life activity is an endless swarming in ordinary house dust, in which they find flakes of dry exfoliated epidermis and eat them.
On a note
For many people, the idea of having such mites in the house may seem like science fiction. Of the entire superorder of ticks, the most famous are ixodid - quite large and found only in the wild (the very ones that are carriers of tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis). It can be difficult to imagine that among their relatives there are those who are not distinguishable without a microscope and can live permanently in an apartment (moreover, in pillows and mattresses) can be difficult. However, this is true.
Dust mites have 8 legs, ontogenesis characteristic of all mites, and body structure typical of the entire superorder. Moreover, their tiny size is not at all something out of the ordinary. The vast majority of mites are precisely microscopic forms, ranging from glandular glands that live in the skin of almost all adults on Earth, and ending with scabies that cause scabies.

On a note
It is thanks to their tiny size that ticks were able to occupy almost all ecological niches on the planet - they process decaying organic matter in the soil, harm plants, parasitize a huge number of animals (including insects), and survive even in conditions in which other creatures cannot live permanently . For example, ticks are known to constantly live in rock crevices on the Arctic islands and feed only a few weeks a year on birds that build nests here (the rest of the time these creatures starve). As well as, for example, a wine mite is known, which settles on a film in barrels of wine and feeds on a floating suspension in such containers.Some mites can even live and multiply inside the human gastrointestinal tract, causing severe illness.
Dust mites have occupied a clearly defined niche - they live near places of rest and permanent habitation of a person and feed primarily on particles of his dead skin. In this regard, they have developed specific features of morphology, physiology and biology, which allowed them to most effectively adapt to this lifestyle.
And they could become good orderlies in human housing, processing household dust, if they didn’t have several harmful and dangerous features, which we’ll talk about a little later.
What they look like: appearance of larvae, adults and eggs
Adult dust mites have a solid translucent oval body with eight limbs. The larvae look exactly the same, only they lack one pair of legs - this pair develops after the first molt.
After molting, the larva turns into a nymph - it looks similar to adult ticks, leads a similar lifestyle, but is smaller and, most importantly, is not capable of reproduction. After several links, the nymph becomes a sexually mature individual (imago).
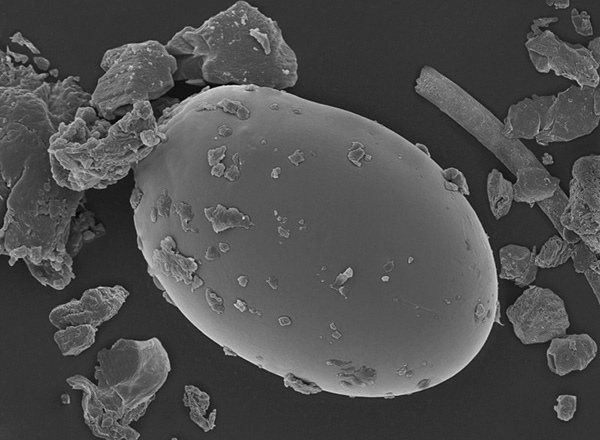
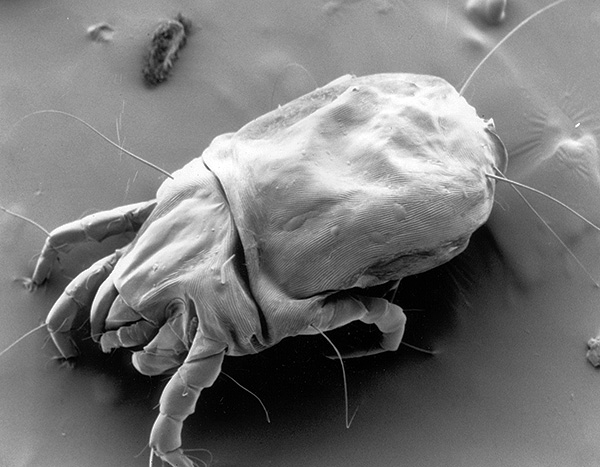
The photograph below, taken with a scanning electron microscope, shows an adult dust mite:
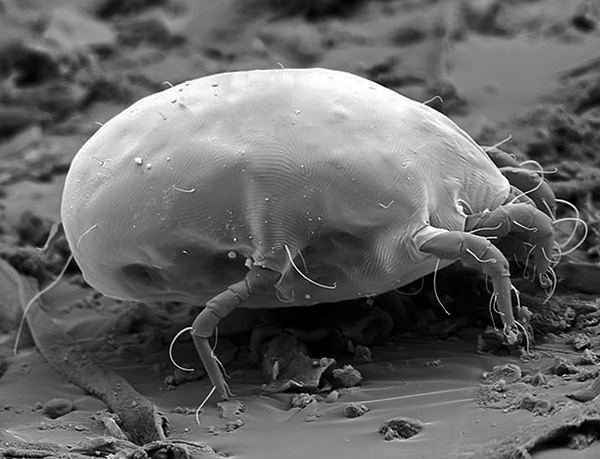
The sizes of adult mites range from 0.3 to 0.5 mm, and given the translucent body, they are practically indistinguishable to the naked eye.
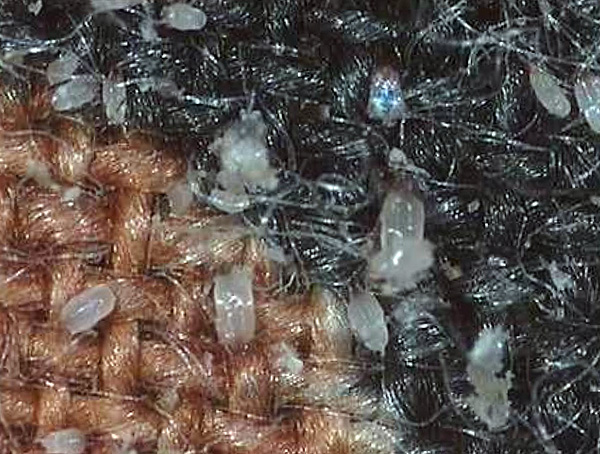
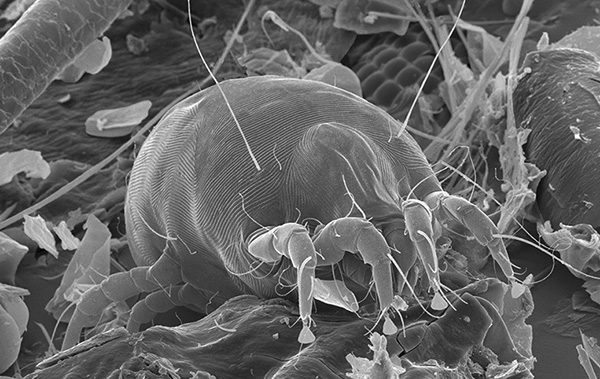
The photo shows a cluster of dust mites in a carpet (this is their favorite habitat, which is why they are often also called carpet mites):

It is interesting
The entire body of dust mites is covered with special hairs and bristles that perceive air vibrations and help to navigate in space. Given that they do not have eyes, it is precisely such organs of touch and a very good sense of smell that allow them to find food and partners for reproduction.
To fix on the substrate, the limbs of dust mites are equipped with suction cups - this allows them to move on almost any surface. They also have special fatty glands, thanks to the secretions from which their body is not wetted by water.
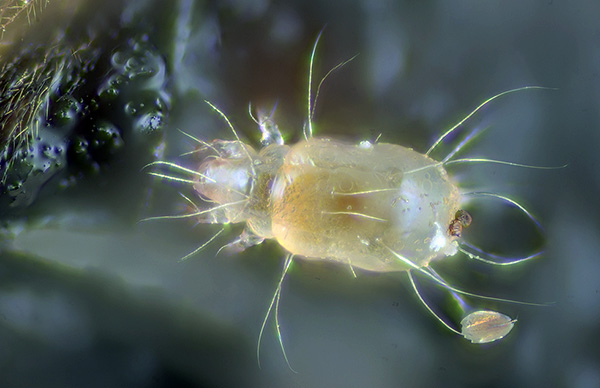
The eggs of dust mites are quite large, reaching up to half the size of the female's body in diameter. They have a whitish color and are arranged in groups - ovipositors.
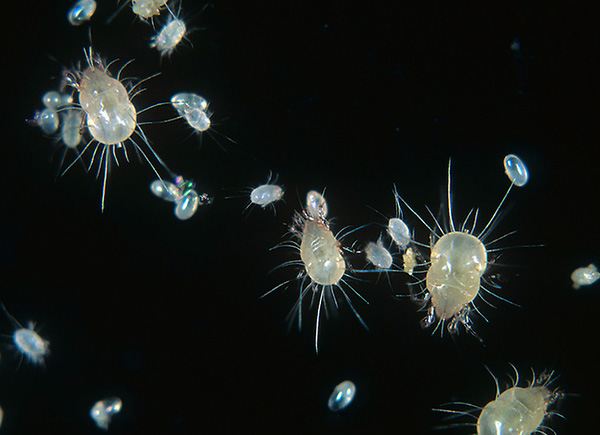

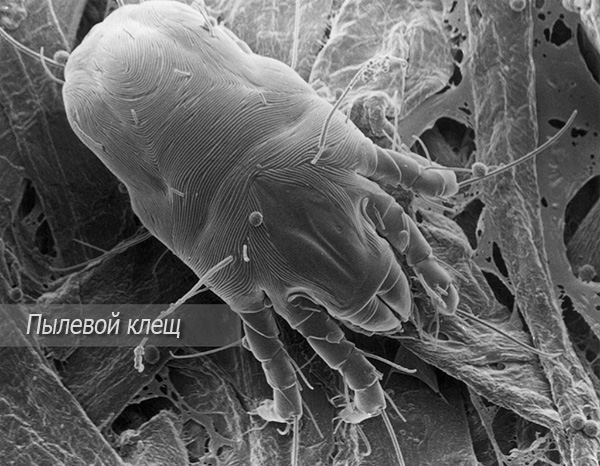
The micrograph shows such an egg at high magnification:

The larva emerging from the egg is very small - up to 0.2 mm. You can only see it under a microscope.
Both larvae and adult dust mites have a well-developed chewing mouth apparatus, for which they are often called chewers. At the same time, they do not have such an extensible cuticle that blood-sucking ixodid ticks have, since they do not need one-time saturation with huge amounts of food. They eat regularly and in small portions.
Nutrition specifics
The basis of the diet of dust mites is the exfoliated epidermis of humans and domestic animals, accumulating in house dust, on beds, in pillows, on mattresses, behind baseboards. Each person loses approximately 1.5 g of dry skin during the day - enough to feed several thousand mites.
Studies have also shown that dust mites actively eat mold fungi, and more than 16 types of mold were found in their diet.Nevertheless, mold is a secondary food object, to which these arthropods switch only when the main food is lacking.
On a note
It is a common misconception that allergies are caused by dust mite bites. In fact, they do not bite humans and animals and do not suck blood. Unlike ixodid ticks, they are not parasitic, and feed mainly on dead human skin particles. Also, they are not carriers of diseases and do not infect either humans or pets with any infections. In addition, they do not spoil food.
As a result, the main concentrations of dust mites in residential areas are found where people and pets spend the most time and where flaky epidermal flakes accumulate in the greatest quantities. Basically, these arthropods concentrate in mattresses, pillows, in dust under beds and behind baseboards, in places where pets rest. At the same time, they are inactive, and practically do not move within the premises - having been born, for example, in a pillow, a tick, most likely, will live in it all its life.
Human danger
Dust mites can cause all three types of allergic reactions in humans - respiratory, contact and food. Due to the specifics of nutrition, they are very close to a person throughout his life, and therefore the allergens they release are likely to enter the human body sooner or later.
For humans, tick excrement is dangerous, having a size of no more than 10 microns.They contain proteins referred to as Der f1 and Der p1, digestive enzymes that help break down dead skin cells so they can be digested. When ingested, the excrement of dust mites very often causes a sensitization reaction, and because of their small size, they often penetrate into the respiratory tract with dust in the air.
The photo below shows ticks in a carpet, with small grains of excrement visible on each individual and on the fabric around them:
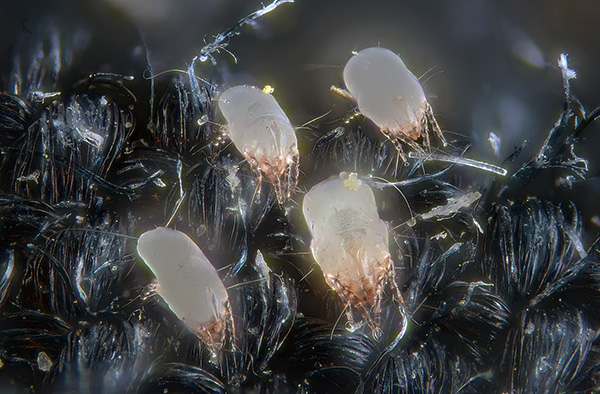
As a result, these pests bring the greatest harm to people suffering from respiratory diseases. Up to 80% of patients with bronchial asthma are prone to tick allergies (in many of them, asthma itself is the cause of persistent rhinitis against the background of allergy to ticks). At the same time, such patients can include people from different age groups: both children, starting from infancy, and the elderly. Many cases of chronic rhinitis and nasal congestion without a runny nose are precisely the consequences of such an allergy.
On a note
It is known that in more than 50% of cases, tick sensitization develops in a child in infancy.
At the same time, the weight of feces excreted by each individual during its life is approximately 200 times the weight of its own body. Thus, the total amount of allergens emitted by the entire mite population in an apartment can be enormous.
During cleaning or just moving a person around the apartment, dust often rises into the air and does not settle for tens of minutes. A person can easily inhale it, after which foreign proteins act on the respiratory organs and cause allergies.
On a note
In the course of research, scientists have found that the development of tick sensitization makes a person more sensitive to other allergens, such as cat and dog allergens. Frequent skin contact with tick excrement can lead to disruption of the barrier function of the integument. Thus, another channel appears for the penetration of foreign biological substances into the body.
It is also worth noting that not only the owners of the premises, but also pets can suffer from tick-borne allergies.
Dead mites and skins of larvae after molting are also dangerous. Chitinous shells, when inhaled by a person, irritate the respiratory tract and also cause allergies.
People who are allergic to dust mites may exhibit the characteristic symptoms of allergic rhinitis:
- Constant itching on the skin, in the nose;
- Rash all over the body (but more often on the face);
- cough, sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose;
- Redness and tearing of the eyes;
- Shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
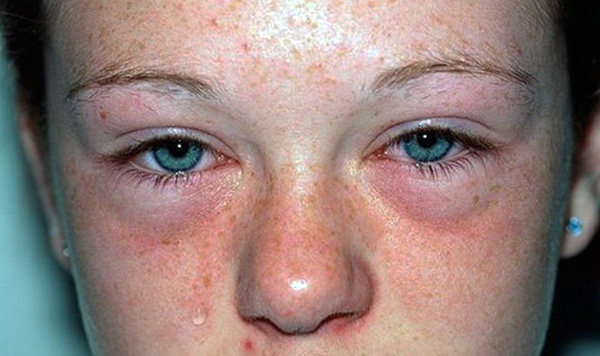
In some cases, there is drowsiness, fatigue, frequent headaches, impaired concentration and decreased performance.
In more severe cases, tick-borne allergy leads to bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, acarodermatitis, chronic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, respiratory allergosis, Quincke's edema.
In patients with bronchial asthma, the condition worsens immediately after going to bed, where the concentration of ticks is usually the highest.
To diagnose tick-borne allergies, an examination by an immunologist is necessary. You will need a blood test for the presence of immunoglobulins - antibodies to dust mite proteins, and skin tests will also be carried out.
Prick tests and patch tests are used for skin testing.In the first case, a liquid antigen is applied to the scratched surface of the back or forearm, and after 15 minutes, the manifestations of a local reaction are studied. In the second variant, the integrity of the skin is not violated, but a patch is simply glued and the changes are assessed after a long time (48, 72 and 96 hours after the start of the study).
The patch test is used to determine the cause of chronic conditions such as contact dermatitis.
In intranasal tests, the allergen is inhaled and the reaction of the nasal mucosa is observed. Tests for conjunctivitis, bronchial test, spirometry and rhinomanometry are used.
With the help of special molecular diagnostics, it is possible to identify which protein the reaction occurs to. Scientists currently identify twenty-four allergens that may be present in dust mites. This is important for the effective treatment of the patient and the selection of the correct method of desensitization.
Allergy symptoms are reduced with the help of medications prescribed by a doctor.
On a note
Also an effective method of treatment is ASIT - allergen-specific immunotherapy. With it, an allergen extract (for example, the drug staloral) is introduced into the human body at certain intervals with a constantly increasing concentration. It is believed that in this case, tolerance of the immune system to the allergen develops, although the exact mechanism of action of such agents is not yet fully understood. It is only known that there is a change in the immune response of T-lymphocytes - special cells of the body that play an important role in the development of acquired immunity.
In any case, treating an advanced allergy to dust mites is much more difficult than preventing the mass reproduction of these pests indoors.
Habitat and lifestyle of dust mites
Favorite microbiotopes of dust mites in a human dwelling are bedding, wall and floor carpets, floor corners, bookshelves, and wardrobe cabinets.

Up to half of apartments in cities are inhabited to some extent by dust mites, of which about 13 different species are known. They are distributed all over the world, and live in almost any premises, regardless of their area and quality of repair. Only species diversity in different regions and population sizes differ. For example, the species Dermatophagoides siboney is distributed only in Cuba - so far it has not been found in other countries.
The European dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and the American dust mite Dermatophagoides farinae are the most common worldwide.
In countries with a subtropical climate, the number of ticks in the premises is the highest, and in mountainous areas the number of individuals in populations decreases with elevation. In hot and dry climates, these pests are less common.
Each locality has its own characteristics of the rate of reproduction of ticks and the increase in the number of populations. For example, in the middle lane, this happens most actively in autumn and spring, and in coastal areas - in spring and summer. It is during this period that it is necessary to carry out measures to destroy ticks and their secretions.
It is interesting
The question remains where dust mites come from in the house. Given their inactivity, it is difficult to argue that they penetrate the premises themselves.It was assumed that they come to dwellings with bird feathers in pillows from various industries, where mites can feed on feather scales in the dust. However, there are controversial points here too: synthetic-filled pillows are also infected with dust mites, although to a lesser extent.
Most likely, resettlement occurs with any already infected things.
No populations of dust mites have been found outside human dwellings. That is, they are typical synanthropic organisms.
The most favorable conditions for the life of dust mites are darkness and high humidity with a temperature of about 25°C. Thus, in rooms with an average relative humidity of less than 50%, ticks are found in 30% of cases, and with a humidity of more than 70% - in 100% of cases.
It is interesting
In the course of studying the migration of dust mites to more humid environments, an interesting pattern was discovered. When setting up the experiment, scientists “offered” to arachnids two paths to moisture, which are no different from each other. And after some time, it was found that most individuals move only along one path for no apparent reason. From this they concluded that there are some special substances that ticks secrete, “showing” the way to the next. The nature of these substances has not yet been elucidated, but perhaps in the future this will help the development of new, more successful methods of combating ticks.
One of the most preferred microbiotopes of dust mites is upholstered furniture, especially the bed. There, a person creates ideal conditions for them by heating the bed during sleep to the optimum temperature with his body (about 8 degrees higher and 7% more humid than the average room).And then he supplies the destroyers of his own health with food - particles of his skin.
Ticks settle in house dust in groups of 10 to 10,000 individuals per 1 gram of dust. A safe concentration for a healthy person is no more than 100 mites per 1 gram. It is at high concentrations (up to 500 individuals per 1 gram) that the development of bronchial asthma and other complications most often occurs.
It is interesting that each of the bedding creates its own, to some extent unique, environmental conditions, which may differ in the size of the colonies and the species diversity of ticks living here.
For example, an ordinary mattress can contain from 100 thousand to 10 million individuals - up to about 140 copies per 1 gram. The frequency of occurrence of pests is the highest here, and it decreases with distance from the source of infection. The lowest concentration is on the floor (on average, about 18 individuals per 1 gram of dust).

Ticks also live in pillows, rugs, carpets, soft toys, paper books, home shoes, clothes, car seats. This is where most of the dust accumulates. And, of course, in a vacuum cleaner, where optimal conditions are created for the reproduction of ticks: a dark enclosed space with poor ventilation and excess food.
Reproduction and life cycle
Due to their small size and little change in mass as they develop, dust mites do not need many resources to grow, which is partly why they have a very high reproduction rate. As a result, in a short time their population in an apartment can reach a colossal number.
Ontogeny - the cycle of individual development - passes from egg to egg in about 15-19 days.During this time, each individual goes through the following stages of development:
- Egg;
- Larva;
- Nymph;
- An adult.
During her not very long life (up to 80 days), the female manages to lay about 60 eggs - one at a time (the egg, due to its relatively large size, can only fit one in her body). Within a few days after laying, a larva hatches from the egg.
The exit of the larva from the egg occurs quite early, when the last pair of legs has not yet formed in the organism. The main function of the larva is nutrition and resettlement, therefore, from the first days of life, it actively moves in search of food. After several feedings, she turns into a nymph. The nymph needs to be molted three times in order to grow to the size of an adult and form the reproductive apparatus, after which it turns into an adult and starts breeding.
On a note
Dust mites have a complex external genitalia. Interestingly, they have special organs - sexual suckers, which play an important role in laying eggs. It is assumed that they perceive the humidity of the environment, which helps to find ideal conditions for future offspring.
Fertilization is spermatophoric: the male spermatozoa are in a special capsule that protects them from external influences. The female, on the other hand, captures these capsules with the help of the external genitalia - after that, for the rest of her life, she will lay about one egg a day.
How to understand that dust mites live in the house?
Due to their small size, these tiny arthropods are impossible to spot with the naked eye.Therefore, usually their presence in the apartment is determined only at the stage of the appearance of allergy symptoms in a person - these can be breathing problems, cough, runny nose, rash and itching, tearing and redness of the eyes, regular headache, fatigue.
More accurate methods are associated with the use of special equipment:
- Counting with a microscope showing adults, nymphs and eggs. In this case, dust and substrates from the places of the most frequent accumulation of ticks are studied - mattresses, pillows, carpets;
- Determination of the content of guanine in dust (guanine is present in the excrement of arachnids) - such an analysis allows us to conclude that these creatures are present or absent in the apartment;
- Immunochemical analysis of allergens, which clearly indicates that the dust contains the digestive proteins of mites.
Independently at home, specially designed chemical test systems will help to detect dust mites. Each of them consists of 10 tests, which allows you to analyze dust from different parts of the apartment in order to find the epicenter of infection. The kit includes a chemical reagent, a test strip, a dust bag and a color scale that can be used to determine the concentration of mites.
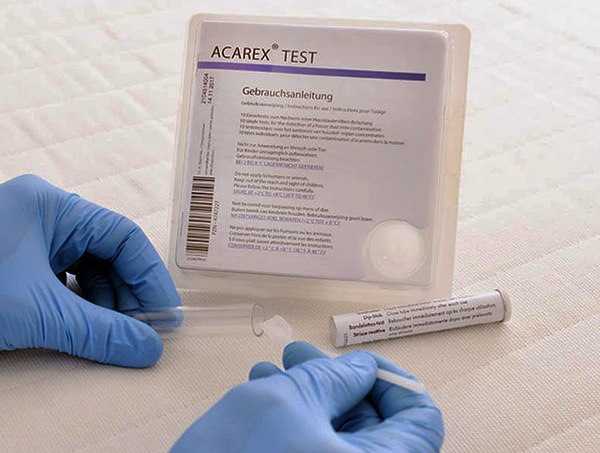
The dust sample is filled with a liquid from the kit, then a test strip is placed in the resulting mixture. A qualitative reaction is carried out, and the color is compared with a reference scale. However, the test is not accurate enough - it only shows how many or few ticks live in the room.

When working with a test system, safety is important. The study must be carried out in a mask and rubber gloves. If the reagent comes into contact with the skin, immediately rinse it with plenty of water.
The price of such a test system is within 3,500 rubles, so it is more rational to use each of the 10 tests for periodic checks during the period of dust mites control.
Methods of destruction
There are many methods to get rid of dust mites in an apartment - they can be divided into chemical and physical methods of exposure.
Chemical methods include the use of various acaricidal and insecticidal agents. Among them are both common drugs (Karbofos, Dichlorvos Neo, Raid against flying and crawling insects, etc.), and more narrowly targeted drugs (Teflobenzuron, Clofentezin, Propargit and others).
Most commercially available insecticidal sprays and aerosols will be effective against dust mites to some extent. However, they can also be toxic to humans, and processing an apartment with them is quite laborious. When using them, first of all, disinfection of upholstered furniture and carpets is required, desacarization in plastic bags of slippers and shoes with a fleecy lining. In general, the processing is carried out in much the same way as when destroying bedbugs or cockroaches (with the only difference that the emphasis is not on finding insect nests, but on areas of dust accumulation).

On a note
Popular are attempts to use folk remedies against dust mites - for example, cumin, wormwood, clove, lavender or tea tree oils (added to detergents). It is assumed that the mites are afraid of the smell of essential oils, but in reality the effectiveness of this method is low.Even if this or that folk remedy is able to repel ticks, they will not disappear from the apartment, because they are physically unable to move a long distance. It will not work to kill them with micro-quantities of essential oils added to water when washing floors.
The physical methods of destruction of dust mites include the action of high and low temperatures.
Experiments have shown that exposure to direct sunlight for 3 hours, as well as temperatures above +60°C or below -20°C for at least 30 minutes, lead to the death of eggs, larvae, nymphs and adults of dust mites. At a temperature of +6°C, egg development does not occur, but their viability can last up to 6 weeks.
Due to this, it is possible to destroy dust mites by washing bedding, curtains, bedspreads and soft toys at a high temperature, as well as by ironing things with an iron or by treating them with a steam cleaner. It should be borne in mind that at temperatures below 40 ° C, up to 93% of individuals remain unharmed.

Things that cannot be washed can be subjected to freezing - ticks do not tolerate cold (below -20 ° C). No less effective is also "calcination" in the sun - ticks die under the influence of heat and ultraviolet rays. Quartzization of the room is partly effective (both due to the action of UV radiation and due to the action of ozone).
Ticks are most sensitive to air humidity - with a prolonged decrease below 40% (for several days), the entire population may die.
Regular washing of floors and dusting also helps - this allows you to destroy most of the arthropods by simply mechanically removing them along with the dust.
The most effective is the use of all of the above methods in combination, and not separately.This dramatically increases the productivity of the activities carried out and helps to get rid of dust mites in the house in a short time.
Prevention of infection of the premises by ticks
The main place in the prevention of infection of the apartment with ticks is the reduction of the amount of dust in the room and, accordingly, the places of its accumulation. This includes moving away from wool carpets in favor of vinyl coverings, replacing heavy curtains and tapestries, storing books and magazines in glass cabinets (all of these places can accumulate dust mites).

Particularly needed:
- Frequent airing of the room;
- Regular wet cleaning;
- Regular cleaning of the vacuum cleaner, air conditioner filters and air purifiers;
- Periodic washing of bed linen at a temperature of at least 60°C.
Ticks live in all types of fabrics, however, as part of preventive measures, it is preferable to use synthetic fabrics, as they are less dusty and better tolerate washing at high temperatures. You can use polyurethane mattresses and pillows with synthetic filler, polystyrene covers for upholstered furniture, eurocovers and mattress covers.
On a note
Studies have shown that dense synthetic materials in 99% of cases block the resettlement and movement of ticks. In the most effective coatings, the pore size does not exceed 10 microns.
Do not forget that dust mites are very sensitive to changes in humidity - this is one of the key factors influencing them. Therefore, maintaining a dry microclimate in the room will significantly reduce the risk of pest populations developing here, and if the apartment is already infected, it will help to remove them.
Interesting video: this is how dust mites look under a microscope




Since I had a lot of humidity in the apartment in which I lived for a while, dust mites settled in my blanket. At first, I felt movement in my legs. Then I realized that dust mites need water or moisture to live and move around. If you dry all the tissues in the house well, then the mites will not have water and, accordingly, they will die.