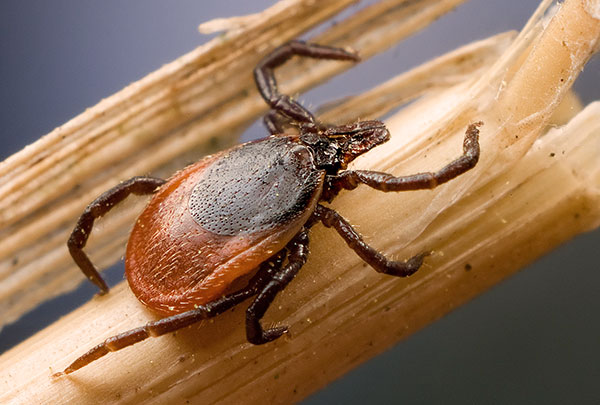

With the beginning of spring, the media are full of information about the invasion of ticks and recorded cases of tick-borne encephalitis. Let's find out in more detail when ticks appear and where they disappear during the year.
The life cycle of ixodid ticks consists of four stages: eggs, larvae, nymphs and adults. Representatives of each of the three active stages spend from several hours to several days on the host, feeding on its blood, and the rest of the time they live in the natural environment. The whole process of development of the parasite often takes several years, so blood-sucking arachnids, like other arthropods, need to wait out the cold season in a state of hibernation. However, the summer heat makes them uncomfortable. All this is related to the frequency of tick activity, which will be discussed in this article.
Diapauses in the life of ticks
In the life of ticks there are periods of inactive existence, which are called diapauses. They help these arachnids survive adverse weather conditions and synchronize their life cycle with changes in the environment.
Only a humid tropical climate is optimal for the continuous development of ixodid. In subtropical climates, summer heat and dryness, as well as winter cold, can slow down the life cycle of mites, and in temperate climates this becomes a pattern.Thus, in the middle latitudes, each stage of development of these arachnids takes at least a year, and in cold regions, the life cycle of the tick can stretch for 5-6 years.
It is interesting
Ticks are highly adaptable. Representatives of the same species, living in a warm area, may not have diapauses and go through the entire development cycle in a year, while living in a cold area, they can develop for more than five years.
Tick eggs mature in about 30-40 days. The hatched larvae seek food for birds and rodents, but are often forced to spend the winter hungry. After feeding, the larva molts and turns into a nymph, which looks like an adult tick, but is smaller. The nymph feeds on larger warm-blooded animals than the larva. She, too, can go hungry for the winter.
Having sated, the nymph undergoes a complex process of transformation into an imago. The restructuring of the organism into an adult can take a considerable amount of time and depends on environmental conditions. Without food, the parasite can live for a very long time at all stages of development, and nutrition starts the process of its transformation into a new stage or the formation and laying of eggs.
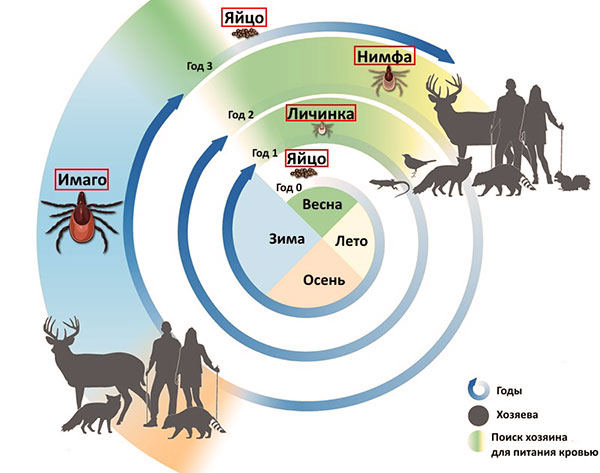
Life cycle of a tick.
There are two types of diapause in ticks: morphogenetic and behavioral. Let's consider them in more detail.
The period of morphogenetic diapause of an arachnid is associated with a slowdown in its development. This is manifested in a delay in the maturation of eggs, engorged larvae and nymphs in this state take longer to prepare for molting, and in females germ cells do not mature. Through this process, the life cycle of the mite is consistent with the change of seasons.
Behavioral diapause is manifested in the absence of aggressiveness in a hungry arachnid, that is, the tick stops looking for prey and attacking them.This behavior is associated with hot weather or preparation for hibernation - engorged individuals tolerate cold worse. Behavioral diapause allows ticks to spend more than a year in a hungry state.
An important role in synchronizing the development cycles of these parasites with seasonal climatic rhythms is played by the photoperiod, that is, the ratio of the length of daylight and darkness. Its change can cause or stop diapause - this process is called a photoperiodic reaction.
The length of daylight that causes a photoperiodic response in some tick species can vary depending on the climate. For example, in a dog tick (Ixodes ricinus) living in Moldova, diapause occurs at daylight hours at 15-16 hours, and in the same species living in the Leningrad region - at 17-18 hours.
In a state of diapause, the metabolic processes in ticks proceed very slowly, and due to the fact that energy is not supplied from the outside, the internal resources of the body are expended. This increases its resistance to environmental conditions such as high or low temperature and low humidity.
When ticks wake up
On the territory of Russia, ticks appear in early spring at an average temperature of +3 °C. As soon as the snow begins to melt, people and animals are at risk of becoming victims of parasites. And some arachnids may not wait for the final melting of the snow cover. After a long diapause, bloodsuckers are very hungry and aggressive.

Ticks on the territory of the Russian Federation begin to show activity at temperatures above +3°C.
On a note
Aggressiveness is the ability of a tick to attack and suck blood. In this state, the work of all the senses of the parasite is directed to the search for prey.
Different regions of the country have their own climatic features, so the duration of diapauses and periods of activity of ticks living there may differ. These arachnids are able to adapt to the peculiarities of the climate and environmental conditions, so the same types of ticks in different places can have completely different behaviors.
In Moscow and the Moscow region, ticks begin to appear from April and attack until mid-June, and the peak of their activity falls on the first weeks of May. In St. Petersburg, located to the north, parasites wake up in early May and most of their attacks occur in the first weeks of summer. And in the south of the country, dangerous bloodsuckers appear in early spring.
On warm spring days, along with the appearance of ticks, the risk of catching infections carried by these parasites increases dramatically. The Rospotrebnadzor service annually registers cases of infection with tick-borne encephalitis and publishes lists of areas endemic for this disease. Traditionally, the first places in them are occupied by the Altai, Perm and Krasnodar Territories, the Republic of Buryatia, Tyumen, Tomsk, Novosibirsk and Sverdlovsk Regions. And in Murmansk, the Kamchatka Territory and the Nenets Autonomous Okrug, the probability of meeting an encephalitis tick is minimal.
Ticks lie in wait for their victims on the tips of grass, branches of bushes, in leafy litter and in burrows. It is important for them to find a place where there will be a high probability of contact with an animal or a person. It also needs to be warm and humid.Therefore, they do not climb trees - it is physically difficult for them to climb so high, the air is drier there and they cannot reach their prey from there, and these arachnids cannot jump.
Bloodsuckers live in all types of forests, in fields and gardens. In the city, in addition to parks and squares, ticks can be found on overgrown wastelands and lawns. They are also attracted to the smell of animals in pastures and watering paths.
Having found a place convenient for hunting, they freeze with a pair of front legs extended forward, on which Haller's sensitive organs are located, trapping odors, exhaled carbon dioxide and thermal radiation coming from the victim.
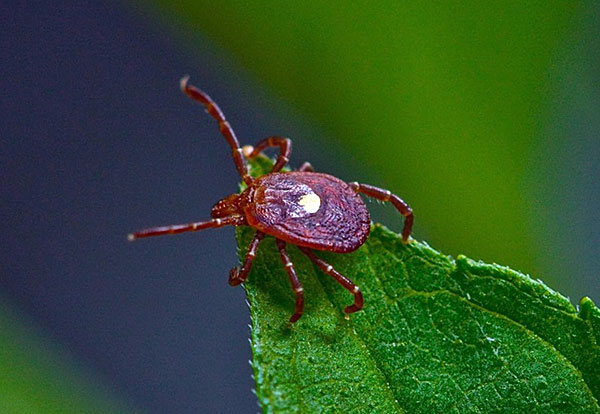

The forward legs of the tick, stretched forward, indicate its readiness for an attack.
It is interesting
Many types of ticks are deprived of sight and hearing. At the same time, their tactile and olfactory organs are so developed that they help to successfully lie in wait for the victim and even run in its direction.
When a person or animal, passing by, touches a blade of grass on which a tick sits, it instantly clings to the wool, feathers or clothes of its prey and begins to search for a place convenient for the bite. The entire lower body and legs of the parasite are covered with spikes, bristles and hooks, which help to hold on tightly to the host and prevent the bloodsucker from shaking off.
The feeding process can last up to 10 days, while the parasite itself increases in size several times. For a bite, a tick chooses secluded places where it is difficult to notice. And thanks to the special device of the oral apparatus, the bloodsucker is attached to the host's body very firmly.
The difference between a hungry and full tick can be seen in the following photo:

The second peak of bloodsucking activity
During the dry summer months, ticks hide from the sun and heat.They have to go down to the roots of plants and climb into the cracks of the soil, where the moisture necessary for their life is stored. Because of this, they have little opportunity to lie in wait for the victim, however, parasites climb onto the grass at night, so even in the hot summer period there is a chance to pick up a bloodsucker.
Ticks reappear towards the end of summer, when the heat subsides, but there is still enough heat and moisture in the air so that they have the opportunity to spend time in wait for prey. Bloodsuckers remain active until sub-zero temperatures are established.
In hot regions of the country, for example, in the Kuban, in the Volga region and in the Crimea, the summer diapause of ticks is longer, and in the Urals, in Siberia, in the Leningrad region, in Karelia and other colder regions, it is short or may even not exist at all. In the latter case, most attacks will occur in June and July.
Winter hibernation care
In mid-autumn, the second peak of flare activity ends, and by November they finally disappear, going into winter diapause. A decrease in temperature and a decrease in daylight hours are incentives for them to search for wintering places. Although parasites are resistant to frost down to -25 °, they are able to withstand it only for a short time.
The most common in Russia dog (Ixodes ricinus) and taiga (Ixodes persulcatus) ticks during the experiments survived at a temperature of -10 ° for about 7 days, and when it was lowered to -15 ° they died after three days. Hungry parasites can endure more severe cold than engorged ones, and eggs are the worst tolerant of frost.
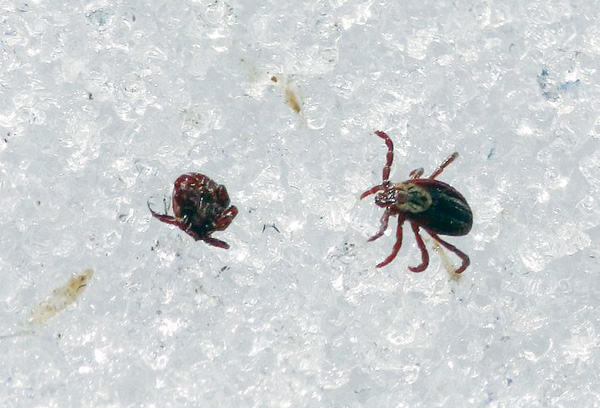

If the tick did not have time to hide, then in severe frosts it quickly dies.
It is interesting
There is a concept of a hypothermia point - if the temperature drops below this value, then ice forms in the body of the parasite and the bloodsucker dies. Depending on the type of tick, the stage of its development and the degree of satiety, it ranges from -6 ° to -28 °.
For wintering, the tick needs to find a windproof place where the temperature will not fall below -6 ° even in the most severe frosts. Therefore, parasites burrow into the forest floor, climb into the voids of the soil or rodent burrows.
On a note
Even in winter, the danger of an attack by a bloodsucker remains. Ticks can enter people's homes and farm buildings along with grass and come out of hibernation due to heat. But you should not be afraid to bring the parasite into the house along with the New Year tree. Ticks do not climb trees, and the cracks in the bark are too small for a reliable winter shelter.
Why ticks are dangerous and how to protect yourself from them
In addition to the tick-borne encephalitis virus, the saliva of the parasite may contain pathogens of many other diseases dangerous to humans, for example, bacteria that cause tick-borne borreliosis, tularemia, tick-borne typhus and some others.
For pets, piroplasmosis, ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are very dangerous, the pathogens of which can also be found in tick saliva. Especially often dogs suffer from these diseases, which can easily pick up a bloodsucker on the run.
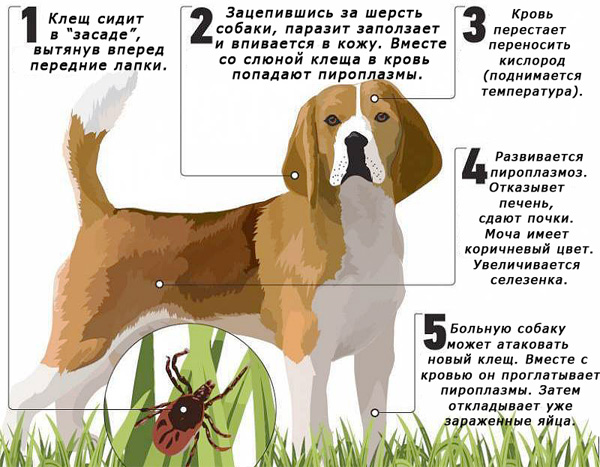
A tick that has bitten a dog can infect the animal with piroplasmosis.
On a note
The longer the tick feeds, the more saliva enters the wound and the greater the risk of infection. Therefore, the attached parasite must be removed as soon as possible.
The tick-borne encephalitis virus infects the human nervous system and brain. Encephalitis is not treated - there is only supportive therapy.This disease is very difficult and almost always leads to disability, and even death. Immunoglobulin, administered after a bite, is not always effective - you can only protect yourself from this disease by pre-vaccination.
Bacteria of tick-borne borreliosis, or Lyme disease, affect all systems and internal organs of a person. This disease is quite simply treated with antibiotics, but in an advanced case it can also lead to disability and even death.
There are simple methods of protection against ticks, and if you follow the following rules, the risk of being bitten will be minimal:
- Close access to the body - clothing should be long-sleeved, and the collar should fit snugly against the skin. It must be remembered that on plain clothes it will be easier to notice the parasite;
- Conduct regular clothing and body checks. A tick can look for a convenient place to stick for several hours, so such an inspection will prevent a bite;
- To refrain from walking in glades with tall grass, not to walk on pastures and animal paths, not to lie down on the forest floor - all these places bloodsuckers love to use to lie in wait for prey;
- Use protective agents that, depending on the composition, can repel ticks or kill arachnids upon contact with the treated surface;
- Take care of the safety of four-legged pets. To protect pets from ticks, there is a large selection of special sprays, drops on withers, tablets, shampoos and collars;
- If the tick is still bitten, it is necessary to remove it as soon as possible. For this, there are special devices - tongs. They can be made by yourself from improvised materials.You can also pull the tick out with a thread or, at worst, unscrew the parasite by picking it up with your nails. After extraction, the arachnid must be sent for analysis.
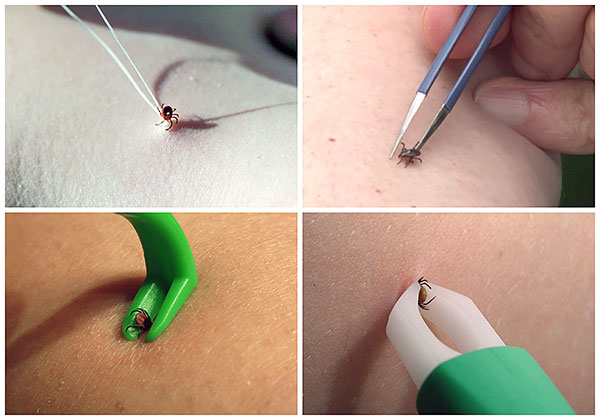
Methods for extracting ticks.
Anti-mite treatment of territories
In some cities of Russia, activities are regularly carried out for anti-mite treatment of squares, parks, territories of kindergartens and sanatoriums. And in Soviet times, the mass processing of forests was carried out using the aviation method. For this, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, or DDT, was used. After exposure to this powerful pesticide, tick populations recovered only after a few years.
However, this practice was abandoned in the 80s of the last century, as it was found that this dangerous substance can accumulate in soil, water and living organisms. Acaricides that are used now are not as strong, but they are much safer for nature and humans.
Owners of country houses and cottages need to take care of the anti-mite treatment of their site. The best time for this is the period when the snow has recently melted. The event must be held before May-June. During these periods, the parasites have already woken up and gone hunting, but have not yet had time to get enough and lay their eggs.
Before processing, you need to check the weather forecast. It is necessary that the day chosen for its implementation be calm, and there should be no precipitation for the next few days, otherwise the product will be washed away by rain into the soil.
Dry grass, leaves, debris, twigs, and logs create a favorable environment for mites and make handling difficult and less effective, so clean up the area first.
As you can see, there are two peaks in the activity of blood-sucking arachnids - spring and autumn, after winter and summer diapauses.It is difficult to give exact dates when ticks will appear - it depends on weather conditions, and in each region the timing of their appearance will be different. Usually these parasites wake up in mid-spring, disappear in June and become active again by mid-August to leave for wintering in October.
The main factors for the appearance of ticks are the melting of snow and the establishment of a positive average daily temperature, as well as a decline in the summer heat. Then the hungry bloodsuckers are sharply activated. However, despite the summer diapause, there is always a chance to pick up the parasite in the warm season. Therefore, going for a walk in nature during this period, you need to constantly remember the precautionary rules.
Video: how to properly prepare for anti-tick treatment



